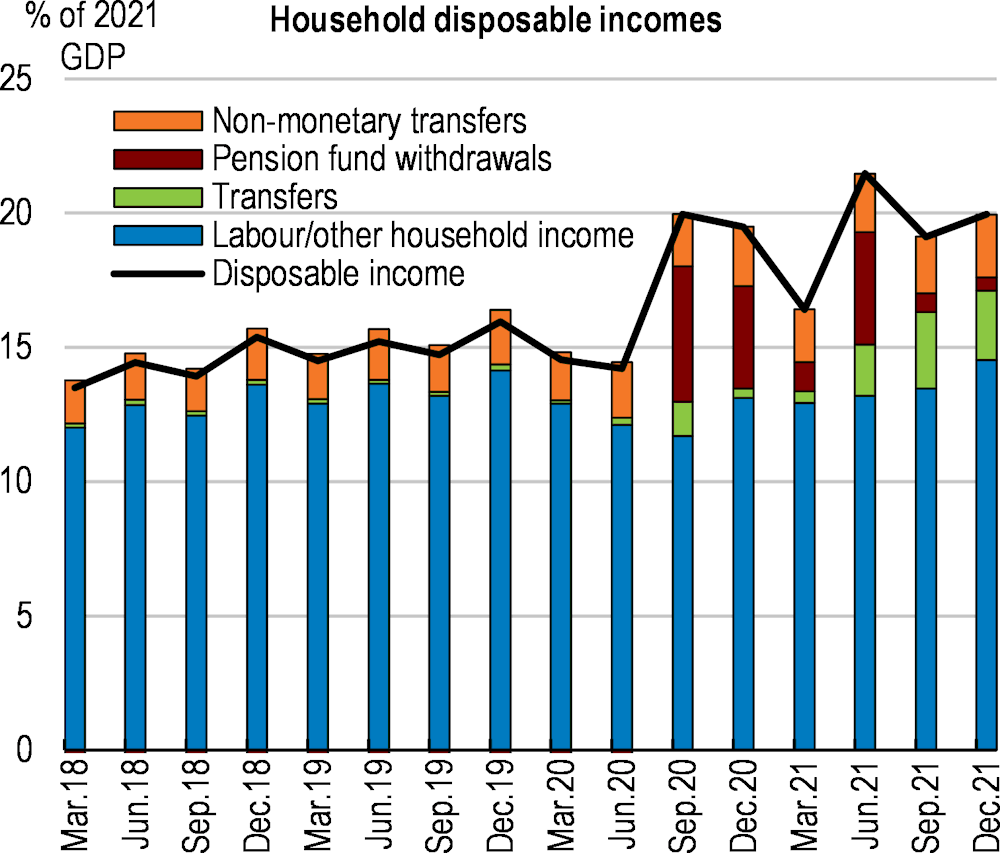
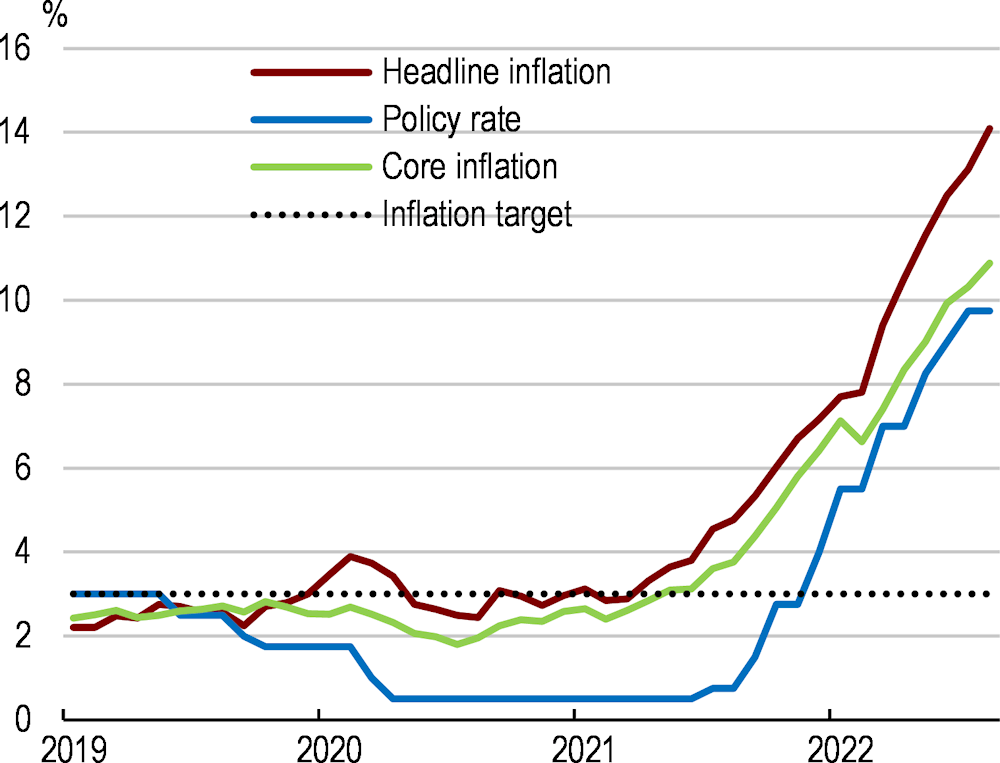
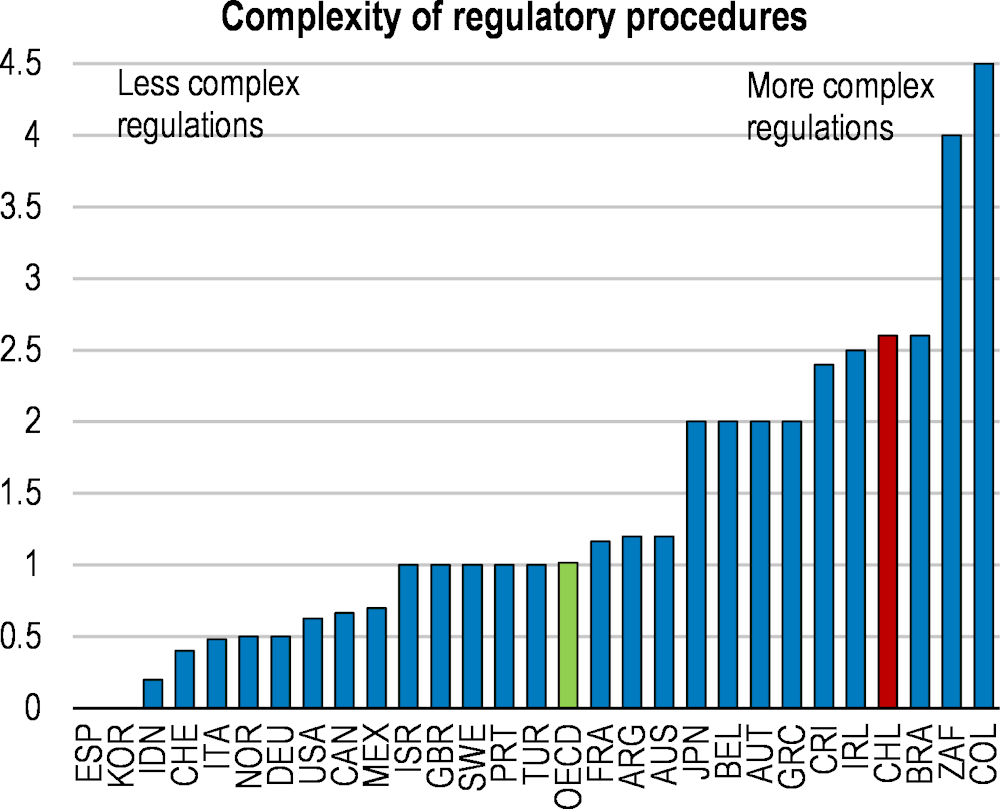
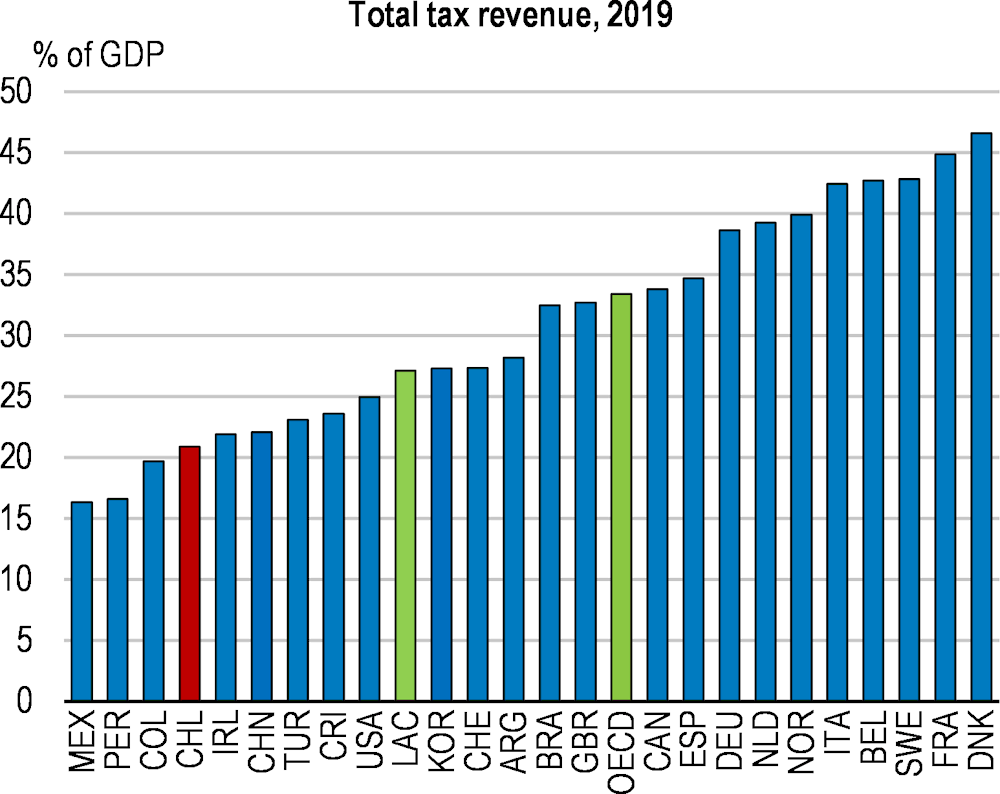
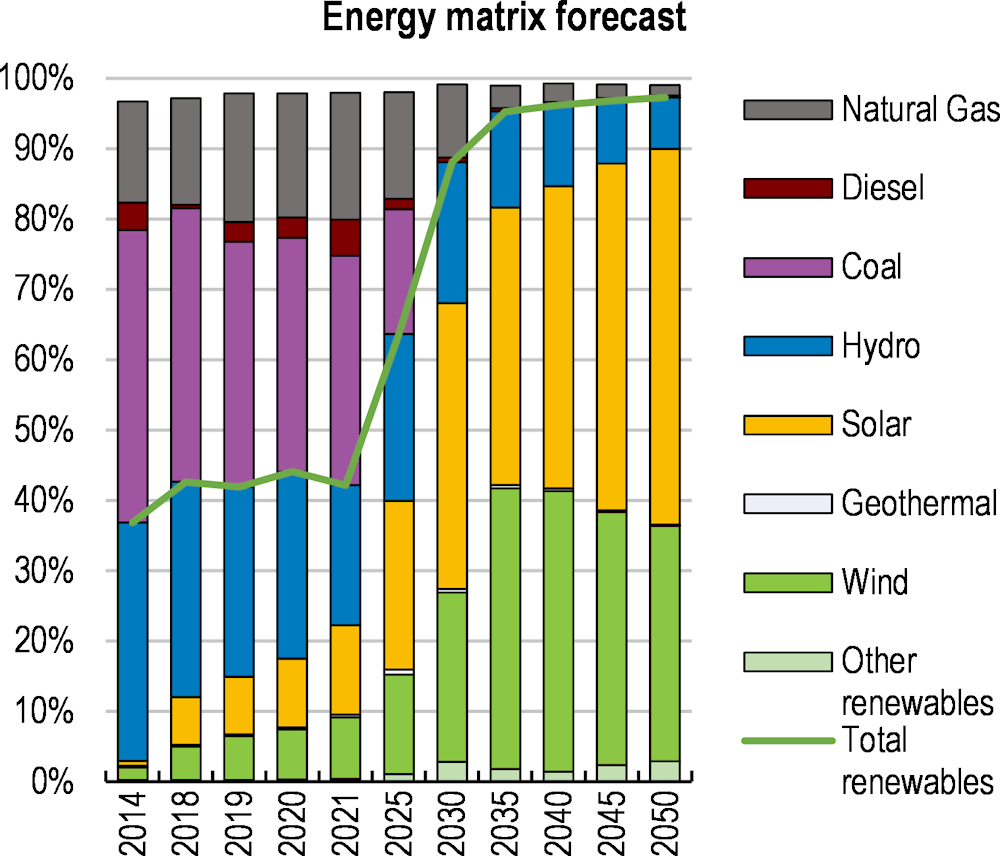
Chile’s economy recovered swiftly from the pandemic on the back of exceptionally strong policy support, which eventually led to a significant overheating of the economy. Inflation has risen amid buoyant private consumption, further aggravated by the Russian aggression on Ukraine. Monetary authorities have acted swiftly to contain inflation, and the fiscal stimulus is being withdrawn. Looking ahead, main challenges for boosting productivity and investment include strengthening competition, reducing regulatory barriers and spending more on research and innovation, while pressing social needs call for more attention to how incomes and opportunities are distributed. Around a third of the workforce is in informal work, which limits their access to social protection benefits. Ensuring a well-defined set of benefits for all, with no distinction between formal and informal workers, will be key. Expanding access to high-quality early childhood education would improve educational outcomes and allow more women to work. Environmental challenges and risks loom large, but also provide significant opportunities for the future. The current high fossil content of the energy matrix contrasts with Chile’s strong potential in renewable energy generation.
SPECIAL FEATURES: RAISING PRODUCTIVITY, EXPANDING SOCIAL PROTECTION, REDUCING LABOUR INFORMALITY