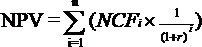The spreadsheet-based Optimising Public Transport Investment Costs (OPTIC) Model is is a simple, easy-to-use decision support tool prepared by the OECD to support the Government of Kyrgyzstan in preparing and estimating the costs and environmental benefits of the Clean Public Transport (CPT) Programme. It was used in particular for costing the replacement of the old bus fleet in urban centres with modern buses equipped with engines that run on:
compressed natural gas (CNG)
liquefied petroleum gas (LPG)
diesel, ideally (imported) Euro 5 fuel
electricity (trolleybuses and battery-powered trolleybuses).
The OPTIC Model was used to estimate programme costs, and the emission reductions of carbon dioxide (CO2) and other pollutants from urban public transport – i.e. carbon monoxide (CO), nitrogen oxides (NOx), particulate matter (PM) and sulphur dioxide (SO2) – that could potentially be achieved by implementing the proposed project pipelines.
Similar models that exist on the market estimate the greenhouse gas (GHG) emission reductions for a country or for groups of countries. These models mainly focus on GHG emissions from industry and take into account various scenarios for the country’s economic development. Such models, however, are not particularly suitable for this investment programme, which focuses on reducing emissions from urban public transport only.