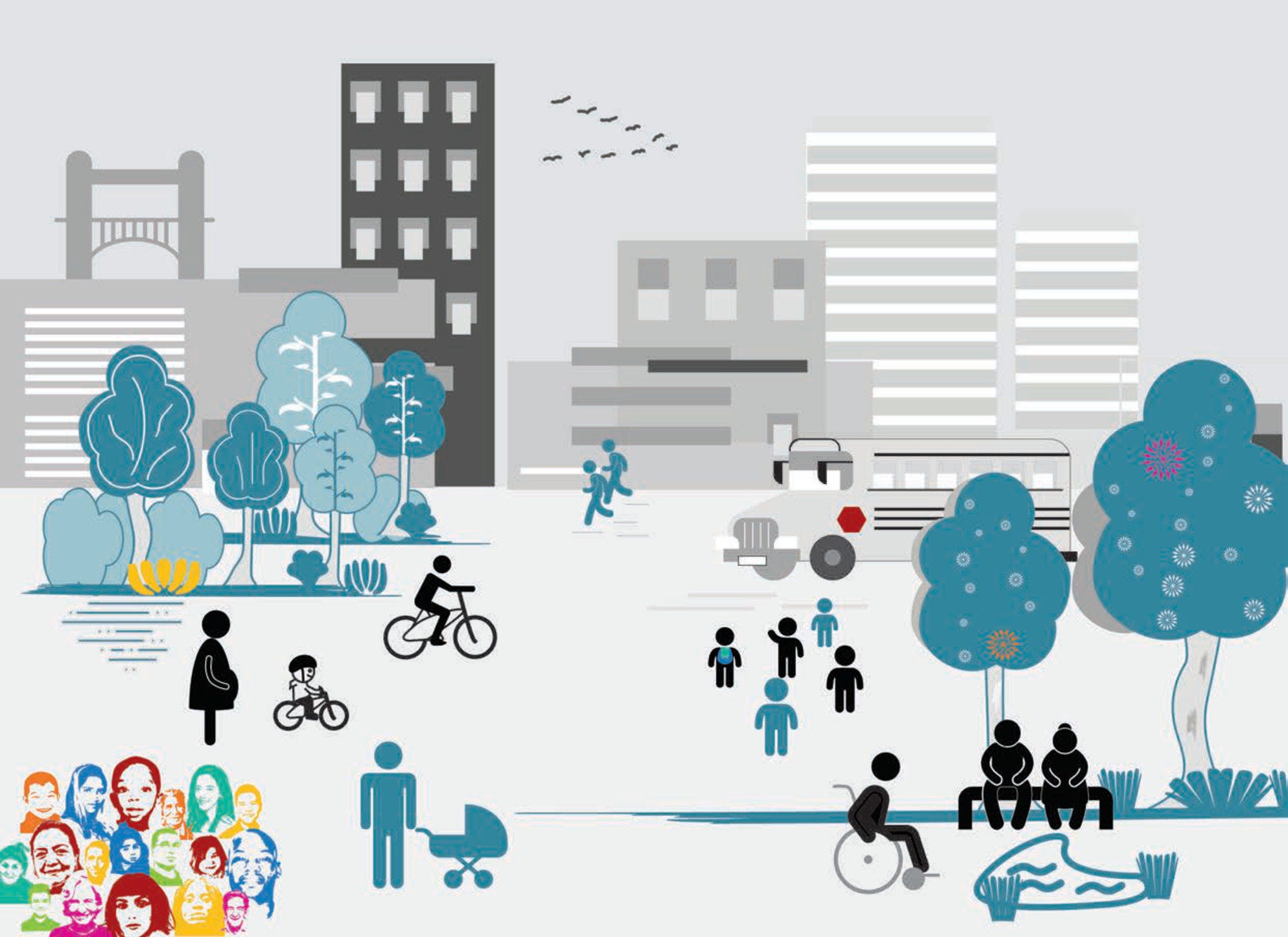
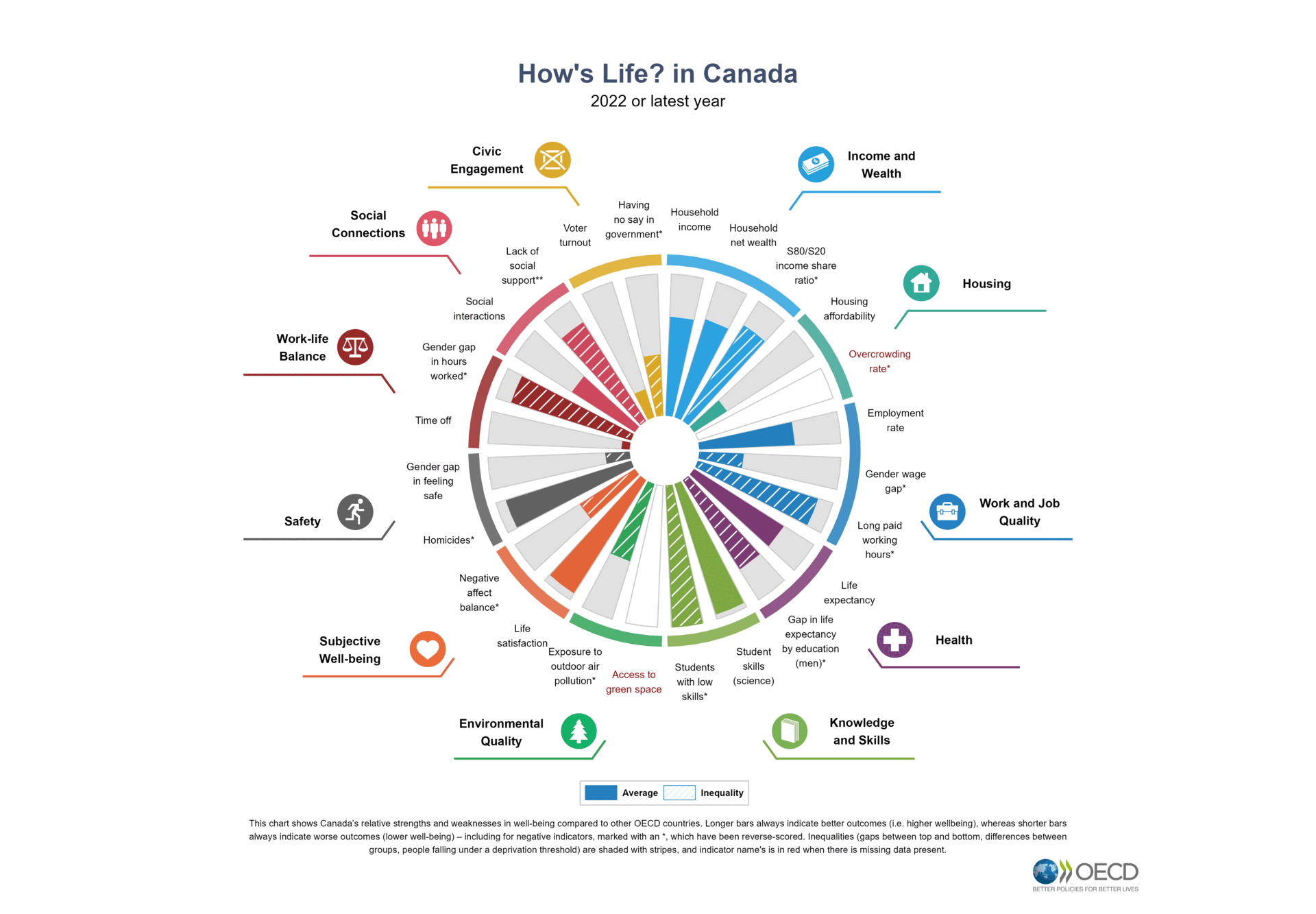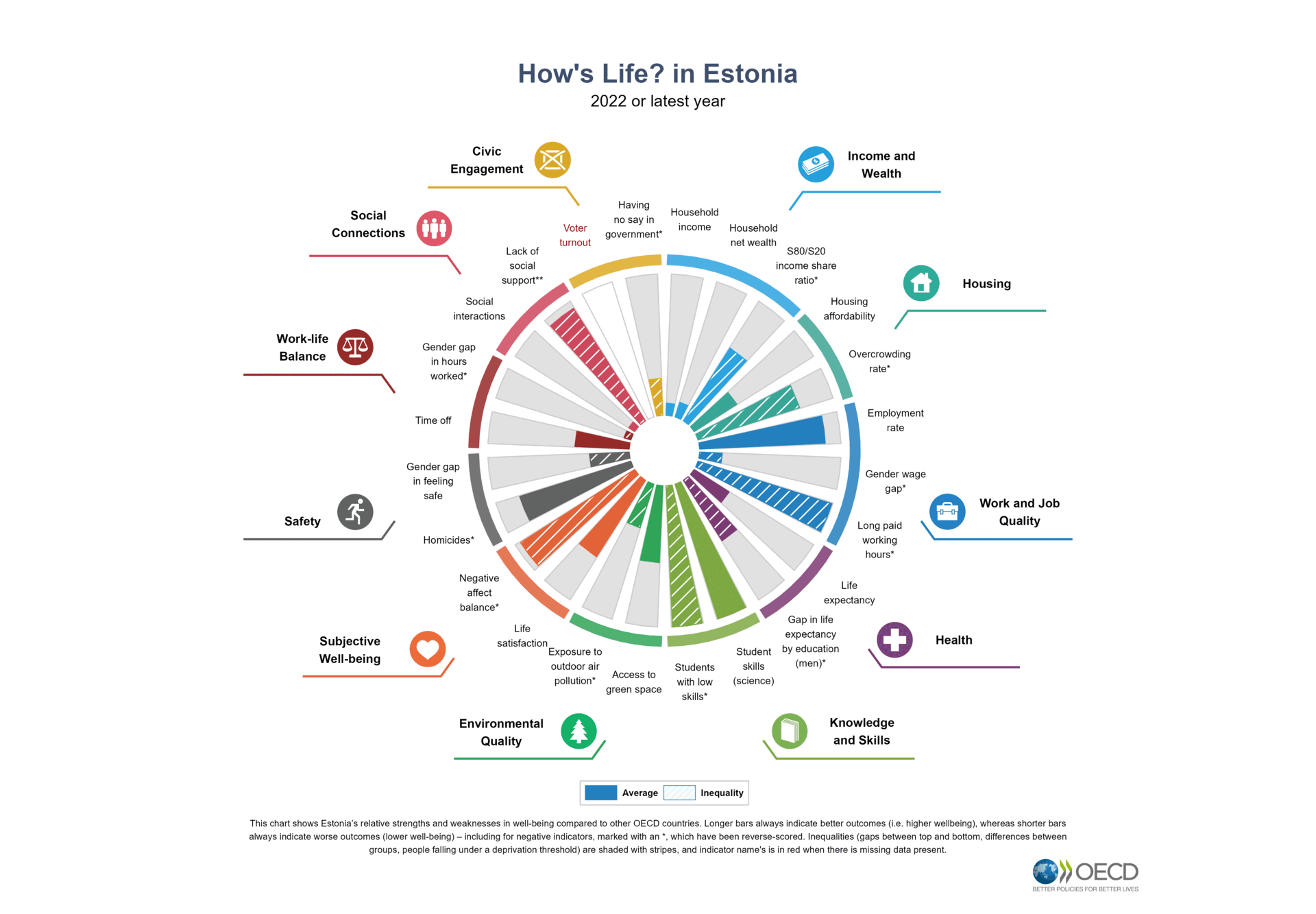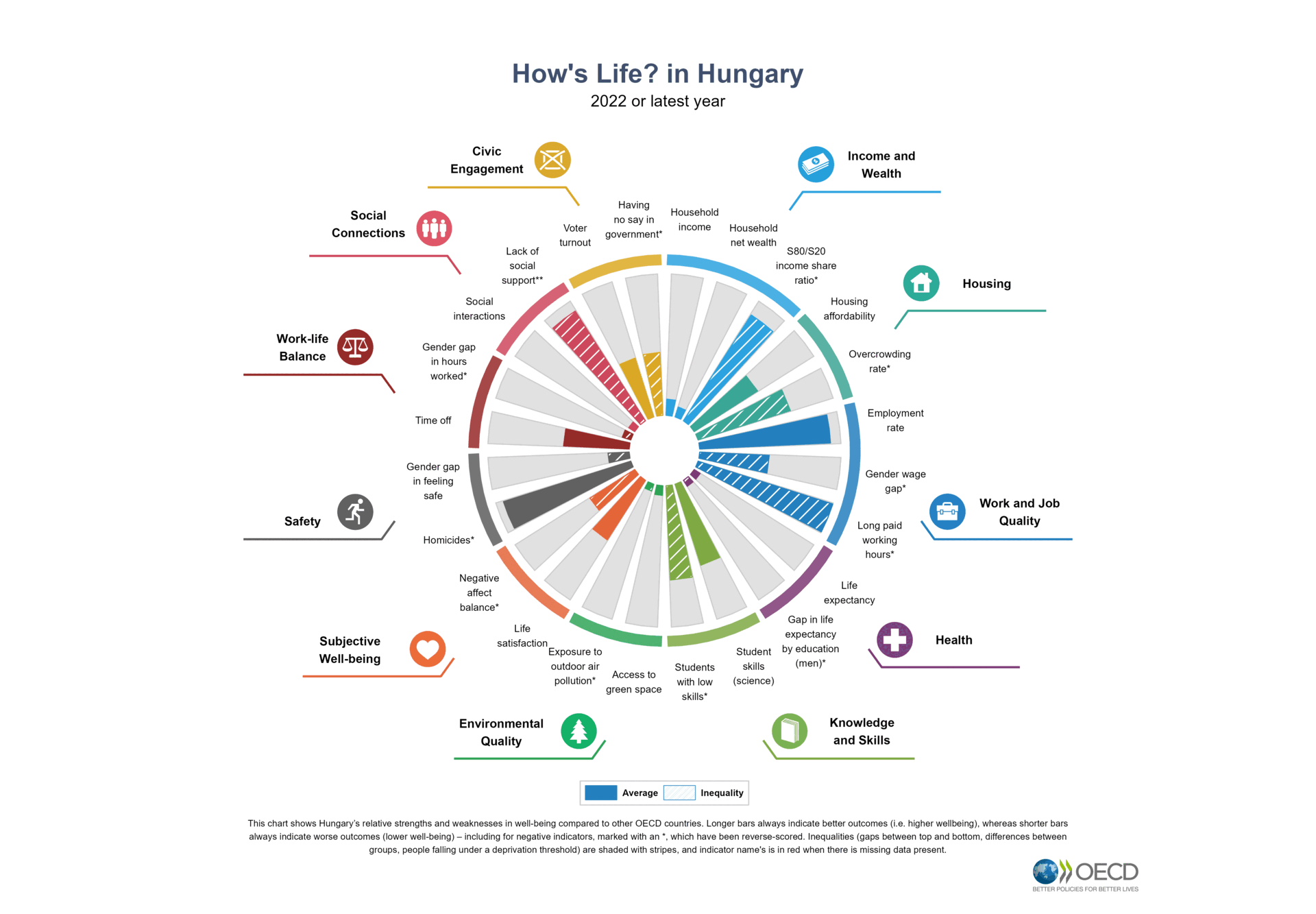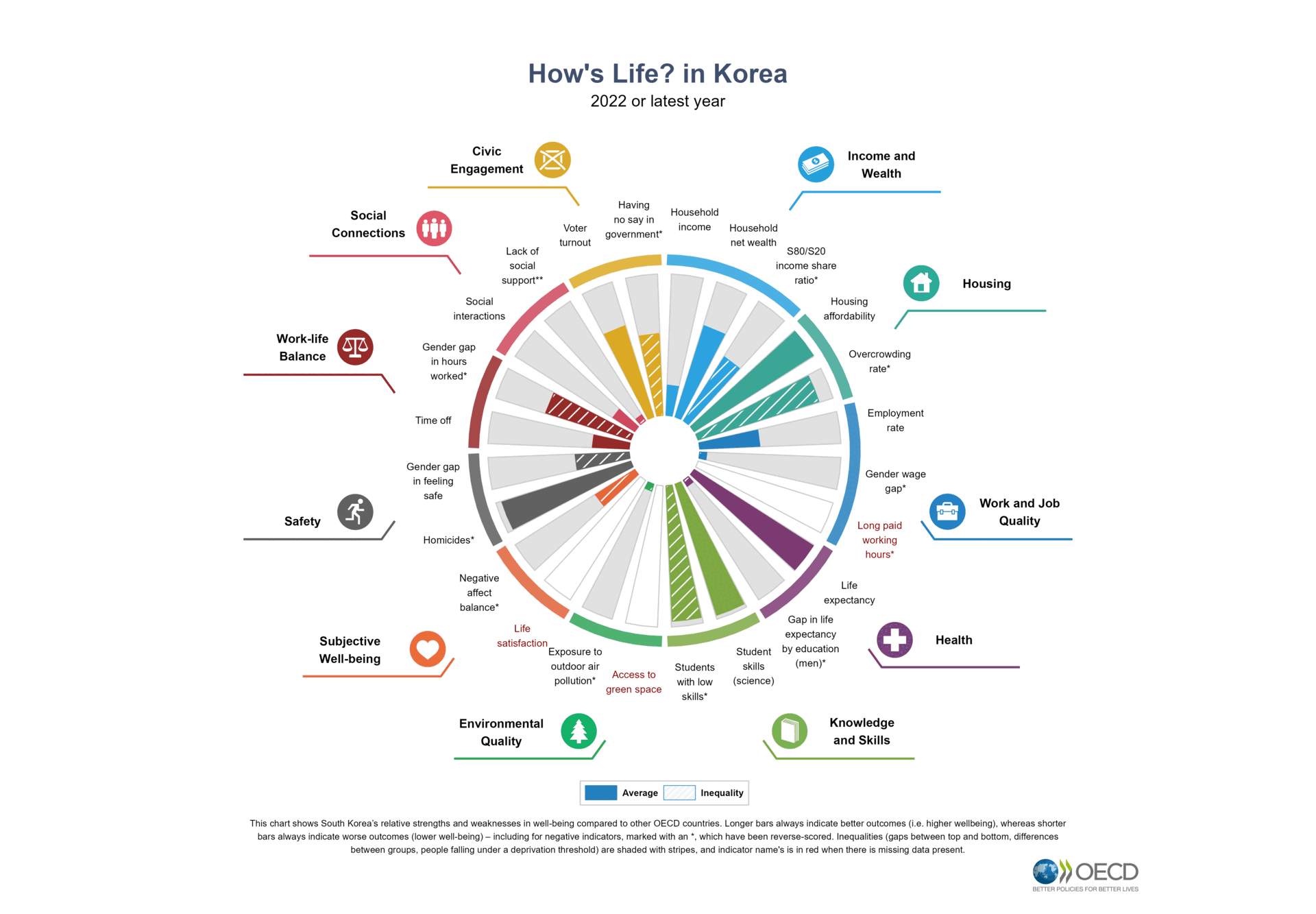
Assessing the well-being of individuals, communities and societies requires looking at multiple aspects that matter for people’s lives. This holistic perspective is even more relevant in a context of fast societal changes. The OECD Well-being Framework considers current well-being outcomes – and inequalities in these – to capture the material conditions that shape people’s economic options, their quality of life, and their relationships. The Framework also includes the systemic resources that are needed to sustain well-being in the future and within planetary and social boundaries. The Framework can support governments and other actors to design policies that promote synergies between economic, social and environmental goals and that put a primary focus on promoting mental health at individual and community level.
The OECD collects statistics on the key components of well-being to monitor people’s quality of life and relational well-being in the context of the digital, demographic and green transitions and to help countries understand whether life is getting better and whether the benefits of progress are being shared equally.