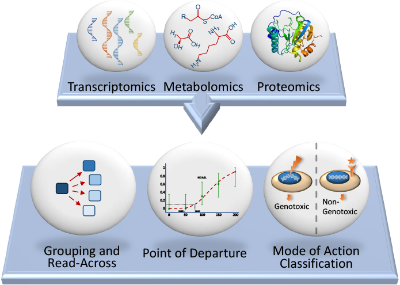
Omics simultaneously measure effects across a range of biological pathways and can be used to investigate a chemical’s mode of action, predict toxicological effects, characterise dose response relationships, and understand species relevance.
The benefits of applying omics approaches include:
- Rapid and cost-effective data generation on biological effects
- Simultaneous investigation of multiple biological pathways
- Measurement of changes to biological pathways before changes in traditional toxicological endpoints occur
- Identification of biomarkers that predict adverse outcomes
- Inform on molecular initiating events and key events in modes of action or Adverse Outcome Pathways via the AOP Wiki.
Applications of omics approaches in toxicology and risk assessment are growing, and include:
- Chemical category formation to support biological read-across
- Mode of action (MoA) analysis
- Comparison of chemical activity potencies
- Derivation of a molecular point of departure (PoD)
The OECD provides a forum for researchers and regulators to collaborate on case studies that are intended to help build consensus on the use of omics platforms in different decision-making contexts.