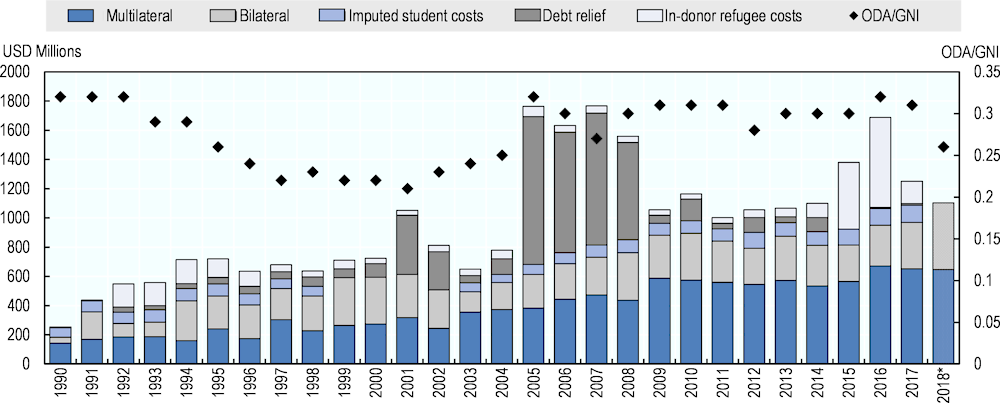
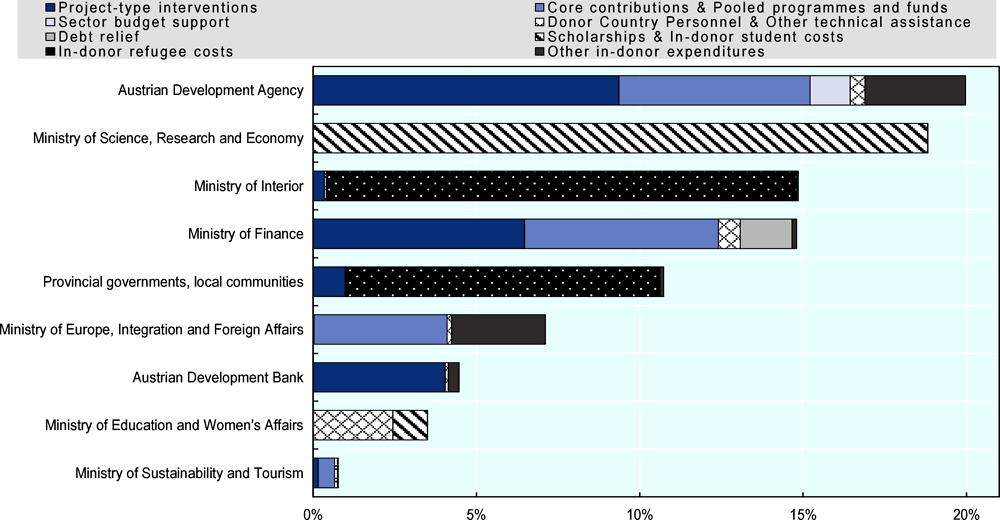
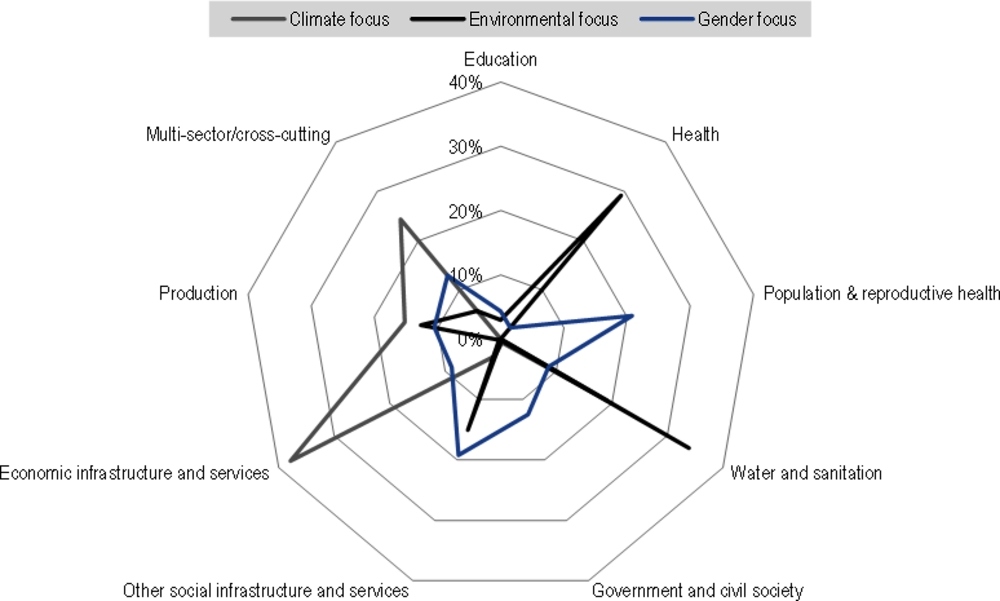
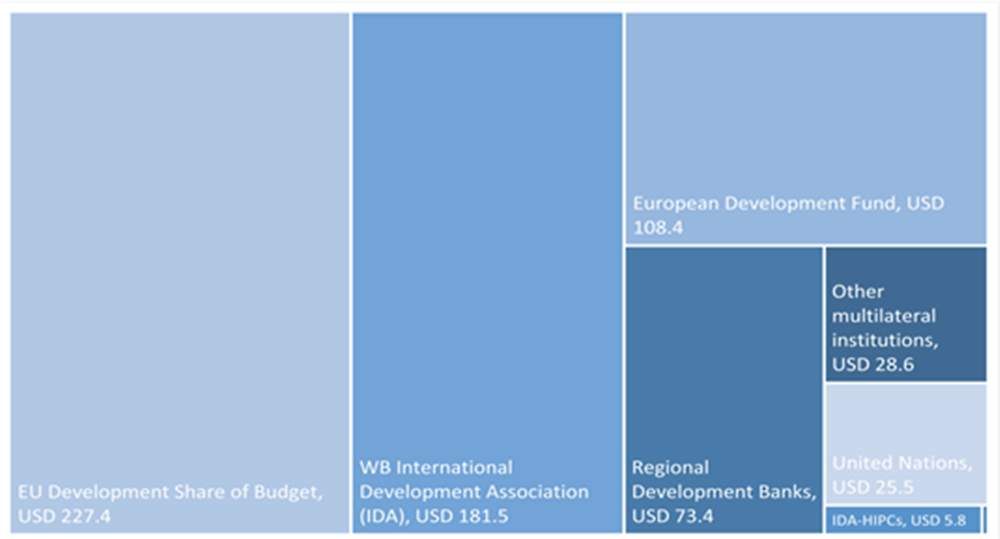
[13] ADA (2013), Business Partnerships Guideline: An Instrument of Austrian Development Cooperation, Austrian Development Agency, Vienna, https://www.entwicklung.at/fileadmin/user_upload/Dokumente/Unternehmen/Englisch/Guidelines_for_Business_Partnerships.pdf (accessed on 22 May 2019).
[11] ADC (2016), Three-Year Programme on Austrian Development Policy 2016-2018, Austrian Development Cooperation, http://www.entwicklung.at (accessed on 1 April 2019).
[21] Clay, E., M. Geddes and L. Natali (2009), “Untying aid: Is it working? An Evaluation of the Implementation of the Paris Declaration and of the 2001 DAC Recommendation of Untying ODA to the LDCs”, Danish Institute for International Studies, Copenhagen, https://www.oecd.org/dac/evaluation/dcdndep/44375975.pdf (accessed on 12 August 2019).
[22] European Commission (2019), “Europe remains the world’s biggest development donor - €74.4 billion in 2018”, Press Release, https://europa.eu/rapid/press-release_IP-19-2075_en.htm (accessed on 13 August 2019).
[5] Fourth High-level Forum on Aid Effectiveness (2011), Busan Partnership for Effective Development Co-Operation, High Level Forum on Aid Effectiveness, Busan, http://www.busanhlf4.org (accessed on 10 April 2019).
[20] Fritz, L. and W. Raza (2017), “Living up to Policy Coherence for Development? The OECD’s disciplines on tied aid financing”, Development Policy Review, Vol. 35/6, pp. 759-778, http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/dpr.12264.
[17] Government of Austria (2017), IFI-Beitragsgesetz 2017, Government of Austria, Vienna, https://www.ris.bka.gv.at/Dokumente/BgblAuth/BGBLA_2017_I_85/BGBLA_2017_I_85.pdfsig (accessed on 26 August 2019).
[15] Government of Austria (2017), Zusammen. Für unser Österreich. Regierungsprogramm 2017–2022, https://www.bundeskanzleramt.gv.at/documents/131008/569203/Regierungsprogramm_2017%E2%80%932022.pdf/b2fe3f65-5a04-47b6-913d-2fe512ff4ce6 (accessed on 2 May 2019).
[19] IMF (2019), Debt Relief Under the Heavily Indebted Poor Countries (HIPC) Initiative, Factsheet, https://www.imf.org/en/About/Factsheets/Sheets/2016/08/01/16/11/Debt-Relief-Under-the-Heavily-Indebted-Poor-Countries-Initiative (accessed on 6 August 2019).
[23] Lammersen, F. and A. Owen (2001), “The Helsinki Arrangement: Its impact on the provision of tied aid”, International Journal of Finance and Economics, Vol. 6/1, pp. 69-79, https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1002/ijfe.144 (accessed on 19 July 2019).
[16] MFA (2019), Working together. For our world. Three-Year Programme on Austrian Development Policy 2019-2021, https://www.entwicklung.at/fileadmin/user_upload/Dokumente/Publikationen/3_JP/Englisch/3JP_2019-2021_EN.pdf (accessed on 25 June 2019).
[18] OECD (2019), Arrangement on Officially Supported Export Credits (January 2019), OECD, Paris, http://www.oecd.org/officialdocuments/publicdisplaydocumentpdf/?doclanguage=en&cote=tad/pg(2019)1 (accessed on 13 August 2019).
[3] OECD (2019), DAC Statistical Reporting Issues in 2018 on flows in 2017, OECD, Paris, https://one.oecd.org/document/DCD/DAC/STAT(2019)11/en/pdf (accessed on 5 August 2019).
[4] OECD (2019), Development Co-operation Profiles, OECD Publishing, Paris, https://dx.doi.org/10.1787/2dcf1367-en.
[2] OECD (2019), International Development Statistics, https://stats.oecd.org/Index.aspx?DataSetCode=crs1 (accessed on 19 July 2019).
[9] OECD (2018), 2018 Report on the DAC Untying Recommendation, OECD, Paris, https://www.oecd.org/dac/financing-sustainable-development/development-finance-standards/DCD-DAC(2018)12-REV2.en.pdf (accessed on 6 August 2019).
[8] OECD (2017), Austria Mid-Term Review, 27 April, Vienna, OECD, Paris, https://www.oecd.org/dac/peer-reviews/Mid-Term-Review-Austria-2017.pdf (accessed on 2 August 2019).
[1] OECD (2015), OECD Development Co-operation Peer Reviews: Austria 2015, OECD Publishing, Paris, https://dx.doi.org/10.1787/9789264227958-en.
[10] OECD (2014), DAC Recommendation on Untying Official Development Assistance, OECD Legal Instruments, Paris, http://legalinstruments.oecd.org (accessed on 12 April 2019).
[7] OECD (2009), Austria: Development Assistance Committee (DAC) Peer Review, OECD, Paris, https://www.oecd.org/dac/peer-reviews/42857127.pdf (accessed on 16 July 2019).
[6] OECD (2004), DAC Peer Review Austria, Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development, Paris, https://www.oecd.org/dac/peer-reviews/34225768.pdf (accessed on 16 July 2019).
[24] OECD (1993), Aid Review 1992/93: Report by the Secretariat and Questions for the Review of Austria, OECD, Paris, https://www.oecd.org/dac/peer-reviews/ (accessed on 28 August 2019).
[12] OeEB (2019), Strategy of the Development Bank of Austria 2019-2023. Financing our Shared Future, Oesterreichische Entwicklungsbank Ag, Vienna, https://www.oe-eb.at/en/about-oeeb/our-focus.html.
[26] OeKB (2019), Financing on Concessional Terms (soft loans), OeKB, Vienna.
[14] World Bank (2019), Remittance Prices Worldwide Database, World Bank, Washington DC, https://remittanceprices.worldbank.org/en (accessed on 6 September 2019).
[25] World Bank (2018), Data on Outward Remittance Flows, World Bank, Washington DC, https://www.knomad.org/publication/migration-and-development-brief-31 (accessed on 6 September 2019).