Digitalisation can be broadly defined as the use of digital solutions and data with the objective to improve business operations, create revenue, transform business processes (not simply digitise them) and create an environment in which data and digital information are in its centre (Peillon and Dubruc, 2019[11]). It has the potential to boost SME development as it increases companies’ ability to reach new markets, optimise and improve their operations, change the way how they engage with their employees. It can help them integrate more easily into global value chains, increase their innovation activity and boost productivity (OECD, 2019[12]). In particular, digitalisation can improve SME competitiveness via the following channels (OECD, 2021[13]):
Digitalisation enables SMEs to more easily access strategic resources. Smaller businesses can leverage a wide range of digital instruments to finance their operations, such as peer-to-peer lending, crowdfunding, and initial coin offerings. SMEs with limited human resource management capabilities access a broader network of job-seekers that meet the desired skills profile.
Digital technologies help SMEs reach a wider customer base and integrate more easily in global markets. Companies’ websites and online e-commerce platforms make it possible to advertise and sell their products to a global audience. Furthermore, digitalisation reduces the costs associated with transport and border operations and makes a wide range of services tradeable.
Digitalisation allows SMEs to achieve scale without mass. Digitalisation of products and services allows SMEs to develop successful digital products and increase their customer bases, revenues and productivity, while significantly bringing down their marginal costs (scale).
Digital platforms enable SMEs to capitalize on network effects. OECD research has shown how digital platforms can deliver positive network effects to SMEs outsourcing business functions, such as advertising, e-commerce and service delivery to online platforms (OECD, 2019[14]).
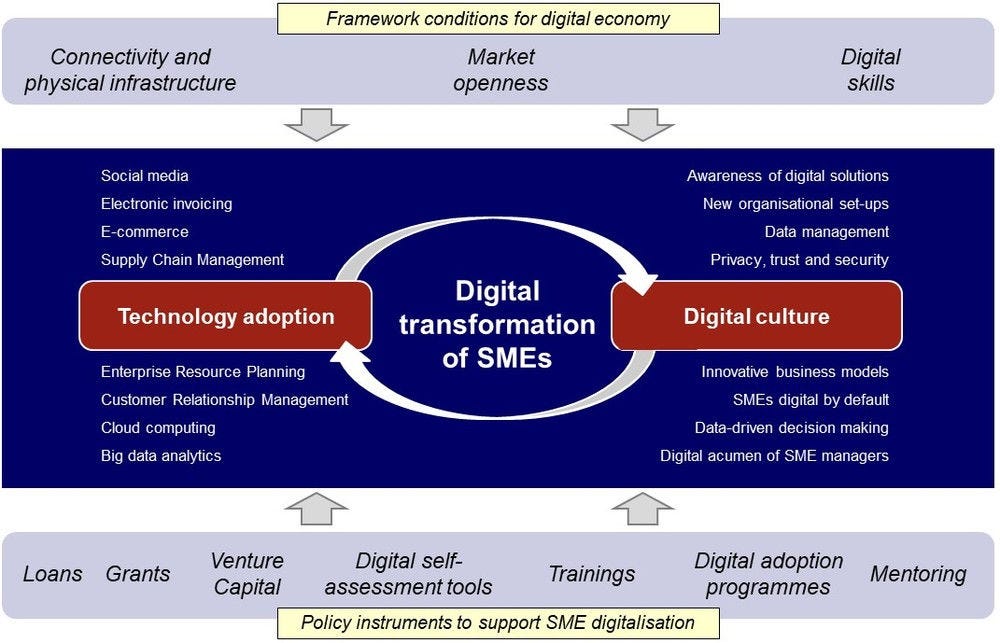
Digitalisation is multi-faceted and often involves the use of application and digital tools and technologies to solve specific problems and improve operations implemented by businesses. Table 2 describes the most common digital solutions adopted by SMEs.
Digitalisation can also improve company performance: businesses decide to invest in digital tools and practices for a variety of reasons, and ultimately the process of technology adoption should bring about tangible benefits for firms undergoing digital transformation. Digitalisation can fuel productivity growth, which in turn brings wage growth, improvements in living standards and more digitalisation. Adoption of digital technologies has the potential to improve SME performance across all sectors, enhance firm productivity and lift living standards.
The COVID-19 pandemic created an unprecedented need to accelerate SME digitalisation as unprecedented quarantine measures highlighted both the limitations of non-digital business models and the opportunity gap between digitalised firms and those who lacked digital profiles.