Effective strategy setting for regional development is a long and complex process. It requires a broadly agreed-upon vision, realistic objectives, high-quality data, and mechanisms to capture synergies across sectors. It also depends on a system to prioritise programmes and plans and ensure that regional development initiatives are clear, targeted, and achievable.
Strategic planning and regional development
We help governments enhance multi-level governance, strategic planning, and policy implementation for regional development. Our aim is to help national, regional, and local governments promote inclusive economic growth and improve resident well-being. We provide all levels of government with concrete recommendations and capacity building tools to help them define long-term objectives, co-ordinate and co-operate with a broad range of stakeholders, and effectively deliver and monitor policies for regional development, innovation, and public services.

Key messages
Close to 30% of the EU’s population lives in cross-border regions. However, these regions face challenges in areas such as public service delivery and support for local economic development. They also tend to perform less well economically than other types of regions. With support from the European Commission, the OECD and five EU cross-border regions are working to strengthen their governance mechanisms and help them deliver on shared development objectives. The work will also result in tools that can help policy makers build more resilient cross-border regions across EU Member States and OECD Member countries.
Regions and cities around the world are increasingly operating in a multi-risk environment. In recent years, governments across the OECD have had to respond to a range of shocks, including pandemics, earthquakes, and armed conflicts. These emergencies highlight the importance of multi-level governance arrangements and subnational capacities for disaster-risk management, reconstruction, and recovery. Recent OECD work on countries such as Ukraine and Türkiye has focused on challenges confronting different levels of government when responding to man-made and natural disasters. These include identifying local needs and reconstruction priorities, involving local stakeholders in the design of reconstruction projects and mobilising and coordinating the support of non-government actors.
Context
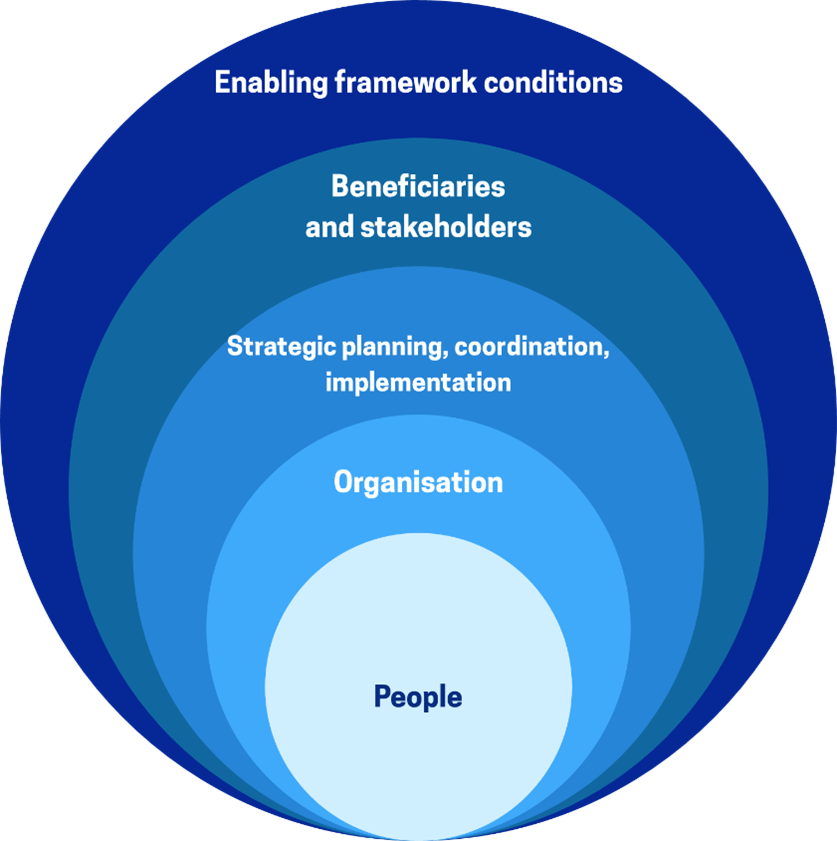
OECD Analytical framework for administrative capacity building
The OECD has developed an analytical framework with five dimensions – people management, organisational management, strategic planning, stakeholder engagement, and framework conditions – to analyse the challenges and capacity gaps facing public authorities responsible for administering and managing public investment funds for regional development, especially EU Cohesion Policy funds. Through work with Managing Authorities from around the EU, we have identified some common challenging areas, such as managing staff, processes, and programmes more strategically and innovatively; mitigating the impact of elements outside of their control on the stability of administrative and investment processes; and ensuring that capacity building of fund beneficiaries is undertaken at the right scale.
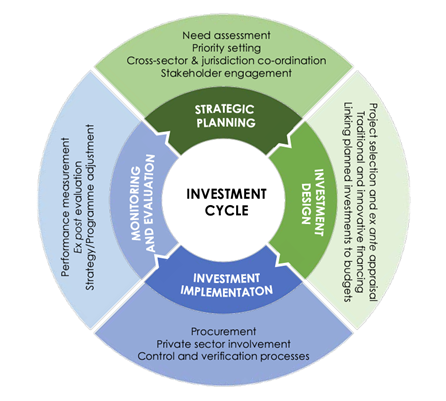
The public investment cycle and investment capacities
Public investment is fundamental to regional development and policy implementation. Effective public investment rests on a strategic public investment cycle, a dynamic process of strategic reflection, planning, implementation, and evaluation. We support national and subnational policy makers refine their strategic processes to optimise regional development policy results.
Related publications
Related events
Programmes
-
The OECD helps governments at every level to better design and implement public investment initiatives that advance regional development, including the delivery of EU Cohesion Policy funds and other public investment funds.Learn more
Related policy issues
-
Industrial transition can set regions on a pathway to growth, equality, and prosperity. This requires an integrated and collaborative approach, embracing innovation, and skills development. However, industrial transition is not a linear process, and is associated with a myriad of socio-economic challenges, including how to overcome higher than average unemployment and population decline, and less than average life expectancy and tertiary education levels. Helping regions in industrial transition re-energise their economic base depends on a mix of policy interventions across multiple sectors – including those advancing the green and industrial transitions – and on governance arrangements that ideally promote experimentation, flexibility and adaptability. We look at how regions can foster economic diversification, growth, and well-being in society to drive successful industrial transition.Learn more
-
Productivity and innovation underpin long-term economic growth and competitiveness of regions. They can help regions transition their economic structures and ensure sustainable wage growth for workers. Regions can follow different paths to unlock their potential, pushing the global knowledge frontier in some areas and focusing on uptake and diffusion of innovation in others. With effective governance, innovation policy can be a lever for place-based regional government. To help regions unlock their productivity and innovation potential, understanding the local drivers for productivity growth, the regional innovation system and its bottlenecks and the interplay with policies at different levels of government is key.Learn more
-
Regional Industrial Transitions to Climate Neutrality supports governments, citizens, businesses and workers in the transformations regional economies need to undertake to reach climate neutrality.Learn more
-
Improving people's well-being requires sound evidence-based policies. We produce indicators for regions, cities and local areas in all areas of well-being. We promote international comparability, as well as the use of cutting-edge methods and new sources of data. Our network of experts advises on best practices for the production and use of high-quality statistics.Learn more






