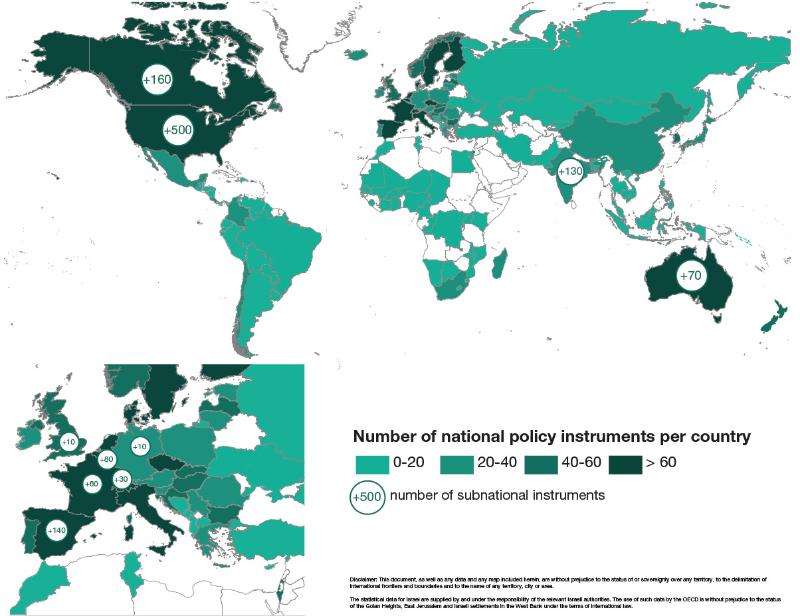
The OECD started building the PINE database in the 1990s, initially with a limited policy scope. Today, the database includes information on taxes and fees, subsidies, tradable permits and offsets, deposit-refund schemes and voluntary approaches relevant to 22 environmental domains. The information in the PINE database is collected via a network of country experts (including government agencies, research institutes and international organisations). Country experts update and validate the data once per year through a password-protected interface. The OECD Secretariat then harmonises and publishes the data in consultation with countries.
The database contains structured and harmonised data. For each instrument, the following information is collected:
- when it was introduced
- what it applies to
- the geographical coverage
- the relevant environmental domains
- the industries concerned
- revenue, cost, rates, exemptions, etc.