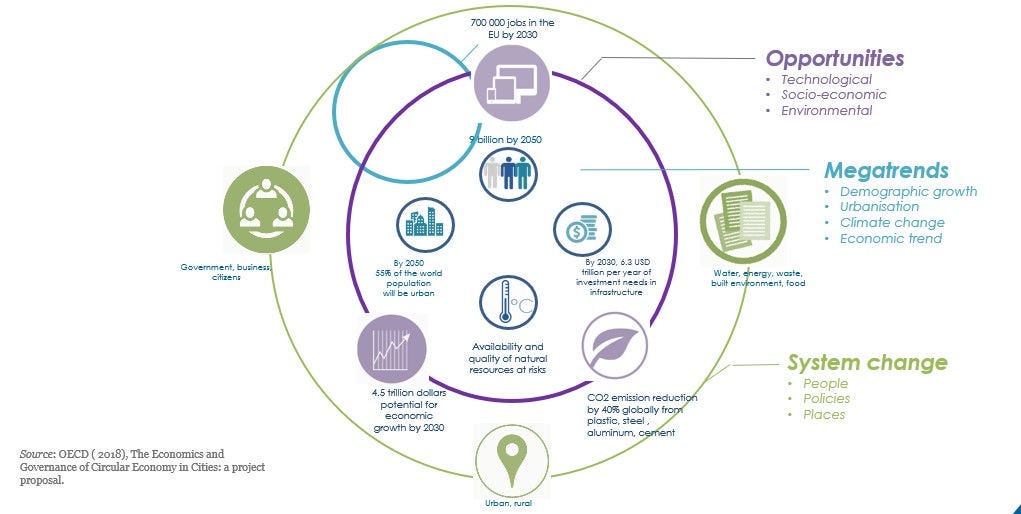
By 2050, the global population is estimated to reach 9 billion people, 55% of which will be living in cities. The pressure on natural resources will increase, while new infrastructure, services and housing will be needed. Already, cities represent almost two-thirds of global energy demand, produce up to 50% of solid waste and are responsible for 70% of greenhouse gas emissions. It is estimated that globally by 2050, the levels of municipal solid waste will double.
Circular economy in cities and regions
Today, cities demand almost two-thirds of global energy, produce up to 80% of greenhouse gas emissions and 50% of global waste. The circular economy is based on three principles: i) design out waste and pollution; ii) keep products and materials in use; and iii) regenerate natural systems. It can provide a policy response to cope with the above challenges, as a driver for economic growth, jobs and environmental quality.
Key links

Key messages
While the circular economy is expected to generate positive impacts on the environment, projections show that shifting from a linear approach of “take, make and dispose” to a circular system is estimated to have as much as USD 4.5 trillion potential for economic growth by 2030. The circular economy could be worth as much as USD 700 billion in global consumer good material savings. Moreover, with activities such as repair, maintenance, upgrading, remanufacturing, reuse, recycling of materials and product-life extension, more labour intensive than the mining and manufacturing of a linear economy, the circular economy is likely to provide job creation opportunities.
Achieving this requires going beyond solely technical aspects. It requires setting the right governance and enabling environment framework. The 3Ps framework (“people”, “policies” and “places”) argues that the circular economy implies a shift towards sustainable production and consumption pathways as well as new business and governance models (people). It also requires a holistic and systemic approach that cuts across sectoral policies, and a functional approach going beyond the administrative boundaries of cities and linking them to their hinterland and rural areas to close, narrow and slow loops at the right scale (places).
Context
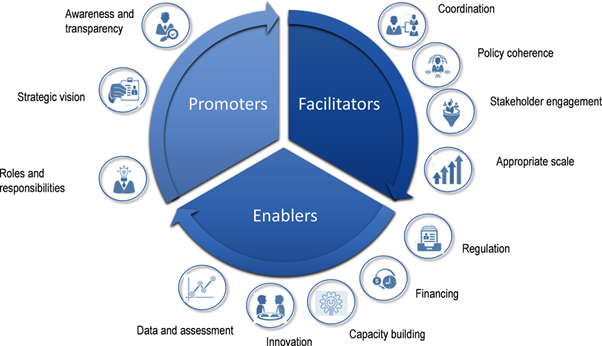
What to do? Promote, Facilitate and Enable!
Cities and regions have a key role to play as promoters, facilitators and enablers of circular economy. The OECD Checklist for Action identifies 12 key governance dimensions, as key conditions for the transition to the circular economy. The OECD Scoreboard on the Governance of the Circular Economy helps governments to self-assess existing enabling conditions for a circular economy, identify challenges and set priorities towards a more effective, efficient and just circular-economy transition.
What can the OECD offer?
Description: The OECD Programme on the Circular Economy in Cities and Regions supports cities and regions in their transition towards a circular economy through multi-level dialogues to identify challenges and opportunities; peer-to-peer learning and key indicators for decision making and evaluation of the circular economy strategies. A number of cases studies highlight the need for place-based policies.
The OECD Roundtable on the Circular Economy in Cities and Regions
The Roundtable will bring together key circular economy stakeholders from cities, regions, national government, business, academia and international organisations to share knowledge, experiences and best practices
- The Circular Economy in Groningen, the Netherlands
- The Circular Economy in Umeå, Sweden
- The Circular Economy in Glasgow, United Kingdom
- The Circular Economy in Valladolid, Spain
- The Circular Economy in Granada, Spain
- The Circular Economy in Ireland
- The Circular Economy in Tallinn, Estonia
- Vers une stratégie d’économie circulaire à Montréal
The Roundtable will bring together key circular economy stakeholders from cities, regions, national government, business, academia and international organisations to share knowledge, experiences and best practices.
- Event: Highlights of the 5th OECD Roundtable on the Circular Economy in Cities and Regions
- Highlights of the 4th OECD Roundtable on the Circular Economy in Cities and Regions
- Highlights of the 3rd OECD Roundtable on the Circular Economy in Cities and Regions
- Highlights of the 2nd OECD Roundtable on the Circular Economy in Cities and Regions
- Highlights of the 1st OECD Roundtable on the Circular Economy in Cities and Regions
Related publications
Related policy issues
-
Brussels Blueprint for affordable cities and housing for all flyerLearn more
-
Cities are hubs of economic growth, opportunity, and diversity, but are also home to wide inequalities. Our work on inclusive growth in cities examines how national and local governments can foster economic growth in cities that is distributed fairly and creates opportunities for all.Learn more
-
Improving people's well-being requires sound evidence-based policies. We produce indicators for regions, cities and local areas in all areas of well-being. We promote international comparability, as well as the use of cutting-edge methods and new sources of data. Our network of experts advises on best practices for the production and use of high-quality statistics.Learn more
-
As places of home, work and leisure, cities play a pivotal role in people’s lives. While being a major contributor to GDP, they also account for large shares of energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions. Now more than ever, resilient, green and low-carbon cities are essential for an economically sound, socially responsible and environmentally sustainable future. Sustainable urban development policies seek to address a range of issues from managing urban expansion and congestion to fostering competitiveness, innovation, social inclusion and environmental sustainability - relevant to the achievement of SDG 11 on Sustainable Cities and Communities.Learn more
-
Our work on urban systems proposes place-based analysis and policy guidance to help cities of all sizes and their regions to address the multifaceted challenges cities face today, including addressing demographic change, advancing decarbonisation, and fostering social justice.Learn more
-
Along with greater opportunity, city life has increasingly meant housing unaffordability, substandard quality, and overcrowding. As the world grows more urban, governments must find creative ways to provide affordable, quality, and sustainable housing for all.Learn more
Contact
Please contact Oriana Romano, Head of Unit, Water Governance, Blu and Circular Economy




