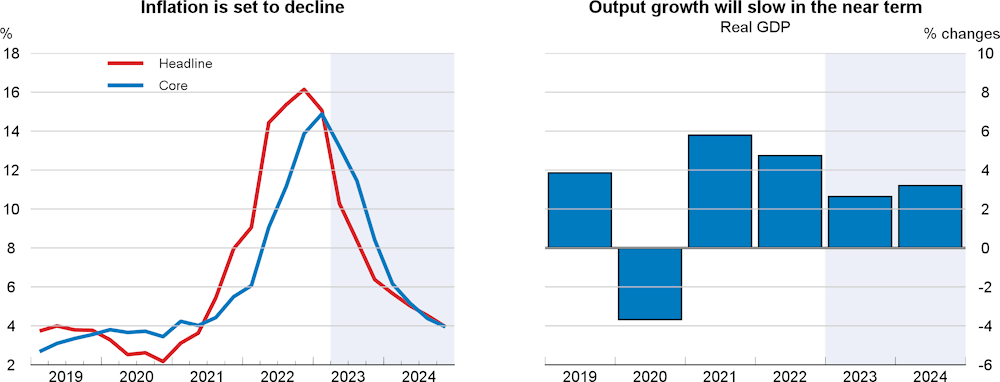
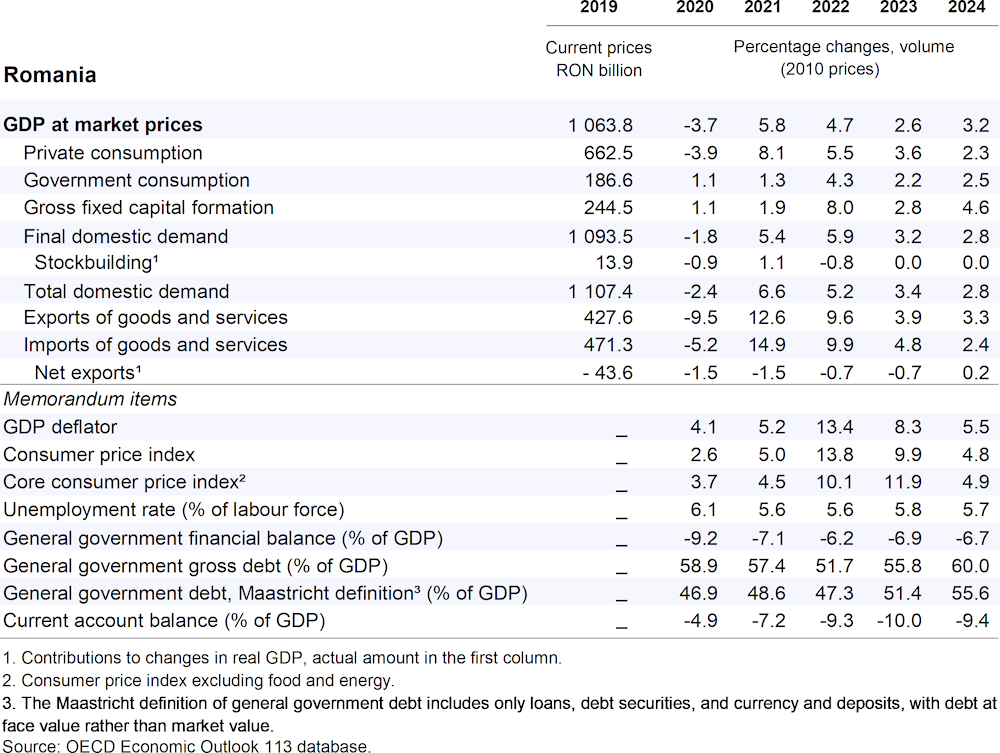
Economic growth will weaken in the near term, reflecting soft demand in the face of continued high inflation, elevated interest rates and subdued growth in trading partners. Recovery, beginning in the second half of this year, will be driven by strengthening household consumption, and foreign demand. The annual increase in output will be 2.6% in 2023 and 3.2% in 2024. The unemployment rate will decline in 2024 but remain above pre-pandemic levels. Consumer price inflation is expected to slow over the next eighteen months but continue to be above target.
Monetary conditions have been significantly tightened and the policy rate should be held at its current level until inflation expectations are durably re-anchored. Fiscal consolidation will be modest in 2024. Longer term, a wider tax base is needed to fund spending on structural reforms, including in health and education while also ensuring fiscal sustainability. Reducing greenhouse gas emissions requires greater renewable energy investment and more energy-efficient buildings. Scope to bring greater numbers of women into employment remains substantial.