OECD Artificial Intelligence Review of Germany

Annex A. Additional figures
Figure A A.1. AI degree programmes in Germany and selected countries
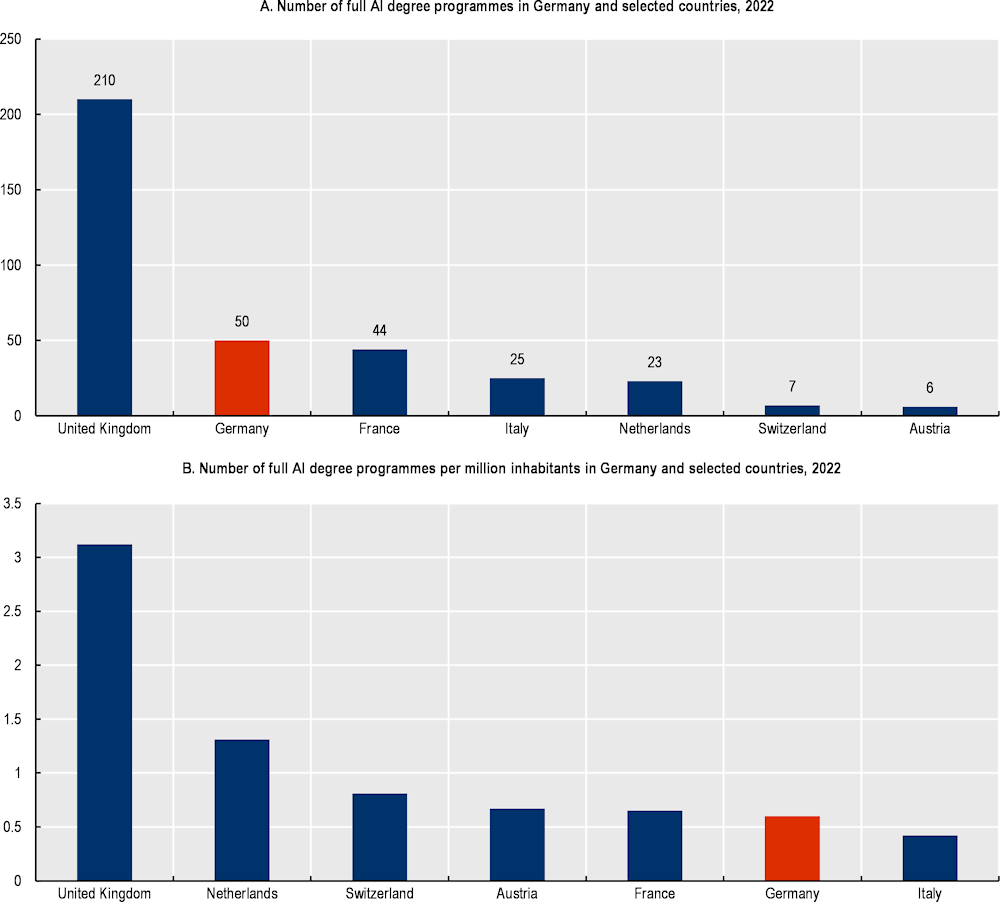
Notes: “Full AI degree programmes” are defined as degree programmes containing in their title “Artificial Intelligence”, “AI”, “Machine Learning”, or “ML” in English or in their national language. The keywords were searched in the study programme databases of the respective countries (e.g. the Hochschulkompass database in Germany).
Source: Calculations based on HRK (2022[1]), Hochschulkompass - Studium, https://www.hochschulkompass.de/studium.html and national sources.
Figure A A.2. AI degree programmes in Germany and selected countries by educational level
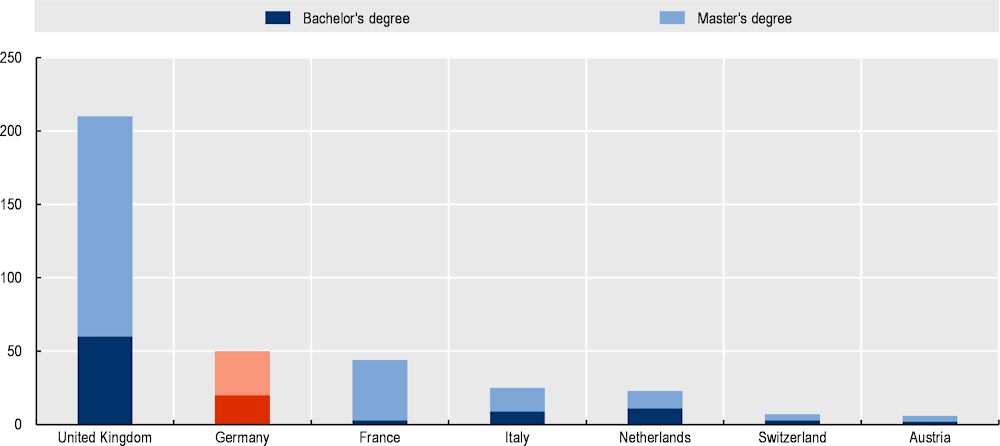
Source: Calculations based on national sources.
Figure A A.3. AI courses are increasingly offered outside computer science departments at German universities
Number of AI courses, per department, 2017/18 to 2022/23 academic years
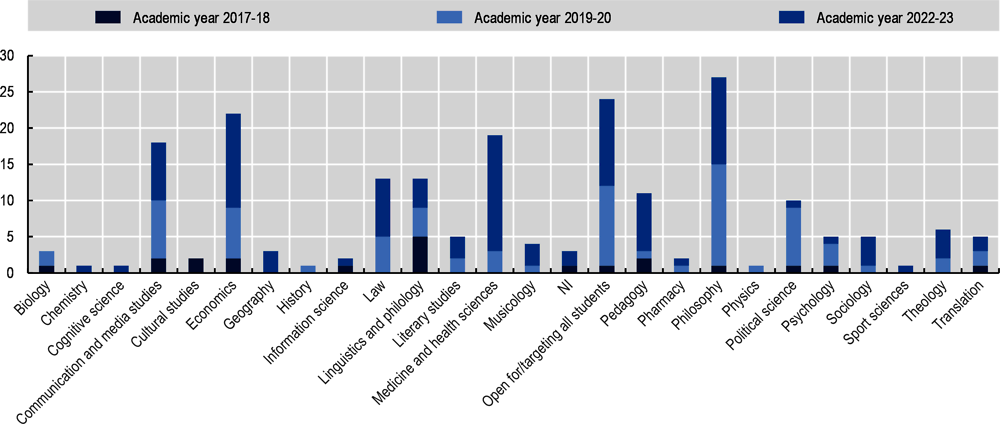
Notes: This graph shows the number of AI courses offered outside computer science departments at German universities for three different time periods. It includes data from the general course registries of the 50 largest German universities in terms of students registered on AI courses for 3 different time periods: academic years 2017/18, 2019/20, 2022/23. For academic years 2017/18 and 2019/20, no data were available for LMU München, Friedrich-Alexander Universität Erlangen-Nürnberg, Universität Leipzig, Justus-Liebig-Universität Gießen, Rheinland-Pfälzische Technische Universität Kaiserslautern-Landau, Universität Augsburg, Hochschule für angewandte Wissenschaften München, Technische Hochschule Mittelhessen – THM, and Hochschule Darmstadt. No data were available for academic year 2019/20 for Heinrich-Heine-Universität Düsseldorf. No data were available for winter term 2017/18 for Julius-Maximilians-Universität Würzburg, and Karlsruher Institut für Technologie. When combining the data for all 3 periods, the courses offered at these 13 universities were removed from each period.
Source: Analysis based on HRK (2023[2]), Statistik - Hochschulen in Zahlen - 2022, https://www.hrk.de/themen/hochschulsystem/statistik/.
Figure A A.4. Vacant online job postings in Germany, by occupation
Percentage change in the distribution of online job postings in Germany after 3 months, by occupation
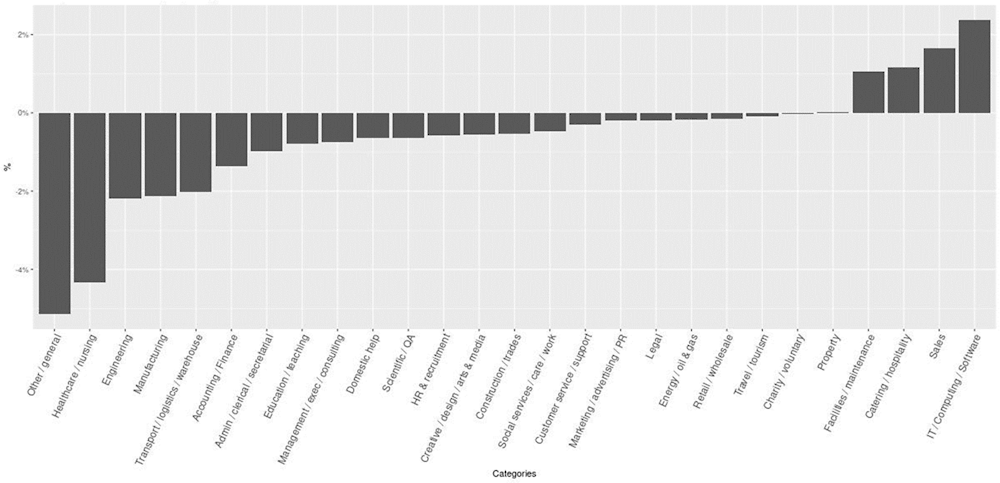
Source: Calculations using online job postings data from Adzuna.
Figure A A.5. Vacant online job postings in Germany, by type of AI skill
Relative percentage change in the distribution of online IT job postings in Germany after 3 months, by type of IT skill
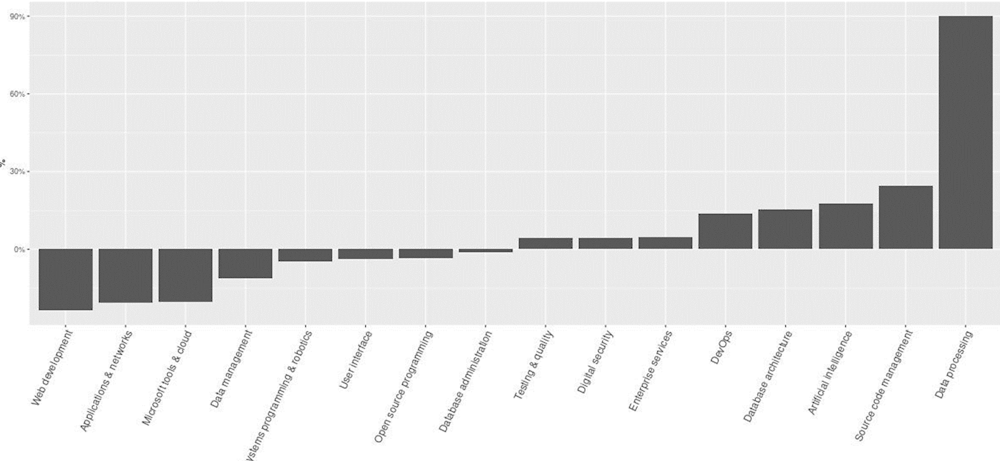
Source: Calculations using online job postings data from Adzuna.
Figure A A.6. Contributions to high impact public AI projects by country
Contributions to high impact public AI projects by country
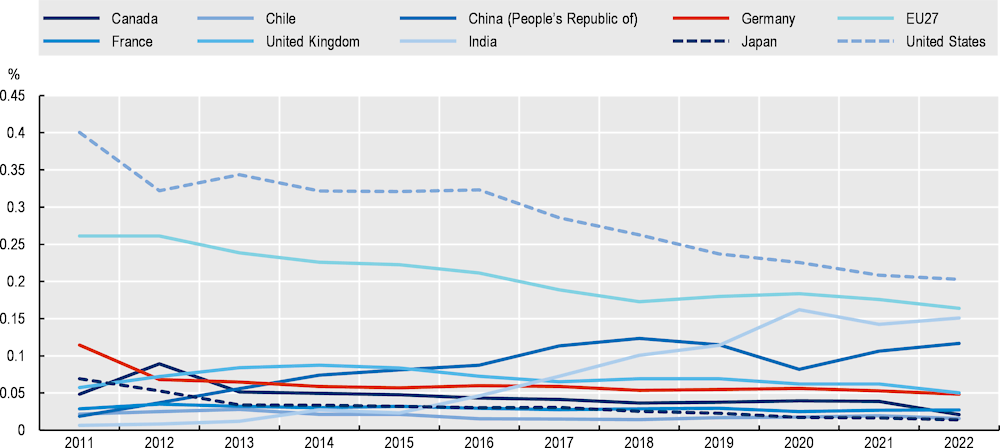
Notes: This chart shows the share of contributions (i.e. “commits”) made to high-impact AI projects (i.e. AI-related GitHub “repositories”) by country and over time. Project impact is determined by the number of managed copies (i.e. “forks”) made of that project.
Source: OECD.AI (2023[3]), Contributions to Public AI Projects by Country and Project Impact, https://oecd.ai/en/data?selectedArea=ai-software-development&selectedVisualisation=contributions-to-ai-projects-by-country-and-project-impact (accessed on 3 October 2023).
Figure A A.7. Speed of fixed broadband subscriptions in OECD countries
Percentage of fixed broadband subscriptions with contracted speed faster than 30 Mbps and 100 Mbps, 2022
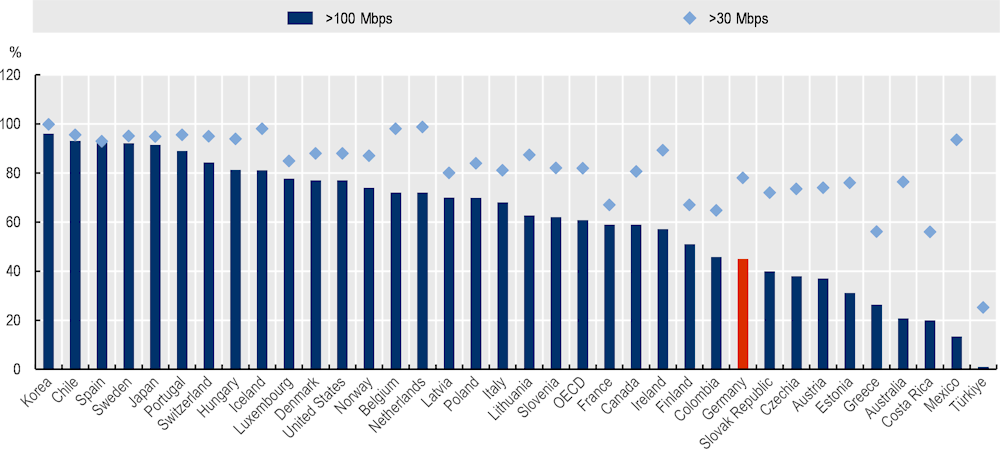
Source: OECD (2023[4]), Broadband Portal, https://www.oecd.org/digital/broadband/broadband-statistics/ (accessed on 3 October 2023).