OECD Development Co-operation Peer Reviews: Germany 2021

Annex A. Progress since the 2015 DAC peer review recommendations
Towards a comprehensive German development effort
|
Recommendations 2015 |
Progress |
|---|---|
|
In updating its National Sustainable Development Strategy, Germany should prioritise a few areas of domestic or foreign policy where it can address incoherence or achieve greater coherence with development benefits. Monitoring progress towards more coherent policies will be required. |
Partially implemented |
Vision and policies for development co-operation
|
Recommendations 2015 |
Progress |
|---|---|
|
To inform development co-operation programming within government and guide partners, Germany should translate the Charter for the Future into an operational framework. |
Implemented |
|
Germany needs to bring its allocation criteria and instruments in alignment with its policy. |
Implemented |
|
BMZ should match its commitment to mainstreaming gender equality and other cross-cutting issues with the leadership, resources and tools needed to deliver. |
Partially implemented |
Aid volume and allocation
|
Recommendations 2015 |
Progress |
|---|---|
|
Germany should set a time-bound path for increasing its aid volumes to meet the 0.7% ODA to GNI commitment. |
Partially implemented |
|
As the development co-operation budget grows, Germany should prioritise increasing support to least developed countries in order to reach the 0.20% ODA/GNI target within the timeframe of the 2030 Agenda, as agreed within the EU context. |
Partially implemented |
Organisation and management
|
Recommendations 2015 |
Progress |
|---|---|
|
To implement the 2030 Agenda, BMZ needs to fulfil its steering function for German development co-operation to the full. Streamlining communication across the entire system would facilitate BMZ’s oversight while reducing transaction costs. |
Partially implemented |
|
BMZ should speed up its programming process and ensure procedures are flexible enough to respond to conditions on the ground, without compromising quality and integrity. |
Partially implemented |
Development co-operation delivery and partnerships
|
Recommendations 2015 |
Progress |
|---|---|
|
To strengthen the predictability of its programmes and strategic planning, BMZ should speed up the process of finalising its country strategies. |
Partially implemented |
|
Germany needs to identify ways of increasing gradually its use of partner country systems, working closely with other development partners. |
Partially implemented |
|
To maximise the impact of its support to civil society and reduce transaction costs, BMZ should consider how to provide multi-year programme funding rather than supporting small, stand-alone projects. |
Partially implemented |
Results and accountability
|
Recommendations 2015 |
Progress |
|---|---|
|
Drawing on its experience with programme results matrices, BMZ should adopt a results-based management system which is fit for its needs of improving decision making and being accountable. |
Partially implemented |
|
BMZ needs to work through how the evaluation set up functions in practice to ensure it gets and makes full use of the independent evidence needed to drive the overall programme more strategically. |
Partially implemented |
Humanitarian assistance
|
Recommendations 2015 |
Progress |
|---|---|
|
To ensure a holistic German humanitarian response, BMZ needs to clarify how its transitional funding and Special Initiatives will be used, and make these funds more predictable and easier to access. |
Implemented |
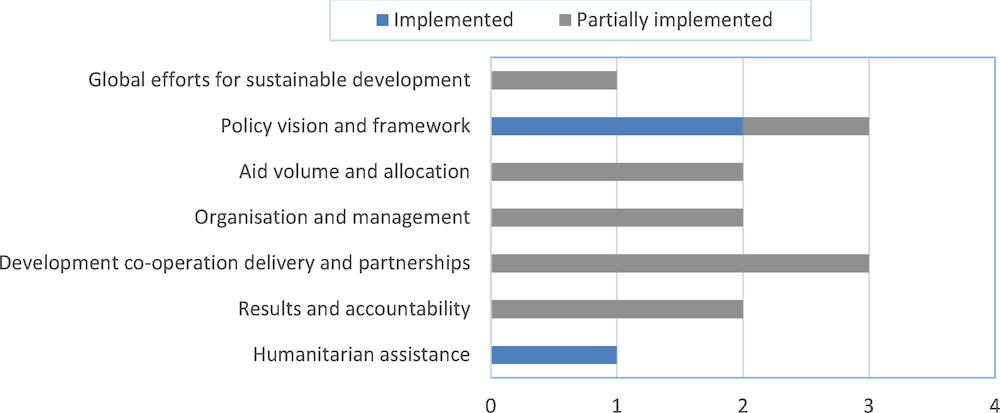
Figure A.1. Germany’s implementation of 2015 peer review recommendations