School funding needs to be allocated in a stable and predictable way so that schools can plan their development over the coming years. Formula funding involves the use of objective criteria with a universally applied rule to establish the amount of resources each school is entitled to. Well-designed school funding formulas are an effective means to distribute funding for current expenditure in a transparent and efficient way. By including weights to distribute additional funds to particular student and/or school categories, formula funding can also play a critical role in aligning the distribution of resources with educational priorities, such as promoting greater equity.
School resources
Well‑designed school funding policies are crucial to achieving quality, equity and efficiency in school education. While the overall level of school funding matters, the strategies used for allocating these funds are equally vital.

Key messages
School autonomy over the use of funds provides schools with flexibility to use allocated resources to fit specific needs. When school autonomy, accountability and support are intelligently combined, they can impact positively on teaching and learning. But the effect of schools' budgetary autonomy on processes and outcomes requires a strengthening of school leadership and management structures, and support with technical budgeting tasks. It is also linked to school size and school network policies. Providing the structures and support to help schools group together and share resources can help achieve economies of scale and a more effective use of funding.
The public funding of private schools is typically combined with parental choice systems that are intended to encourage greater quality and variety in the types of education on offer. To counteract adverse effects on equity, school systems should require all publicly funded providers to adhere to the same regulations regarding tuition and admission policies, monitor adherence to these regulations, ensure transparency and accountability for the use of public funding by providers, and provide all families with adequate access to information and support so that they can make informed choices for their children.
Context
Frameworks for allocating public funding to schools
Formula funding plays an important role in the amount of resources received by public primary and lower secondary educational institutions from local governments. However, local governments make a greater use of administrative discretion, incremental costs, and bidding and bargaining to allocate public funds than is the case at higher levels of government.
Basis used to allocate funding to public primary educational institutions, by category of funding (2019)
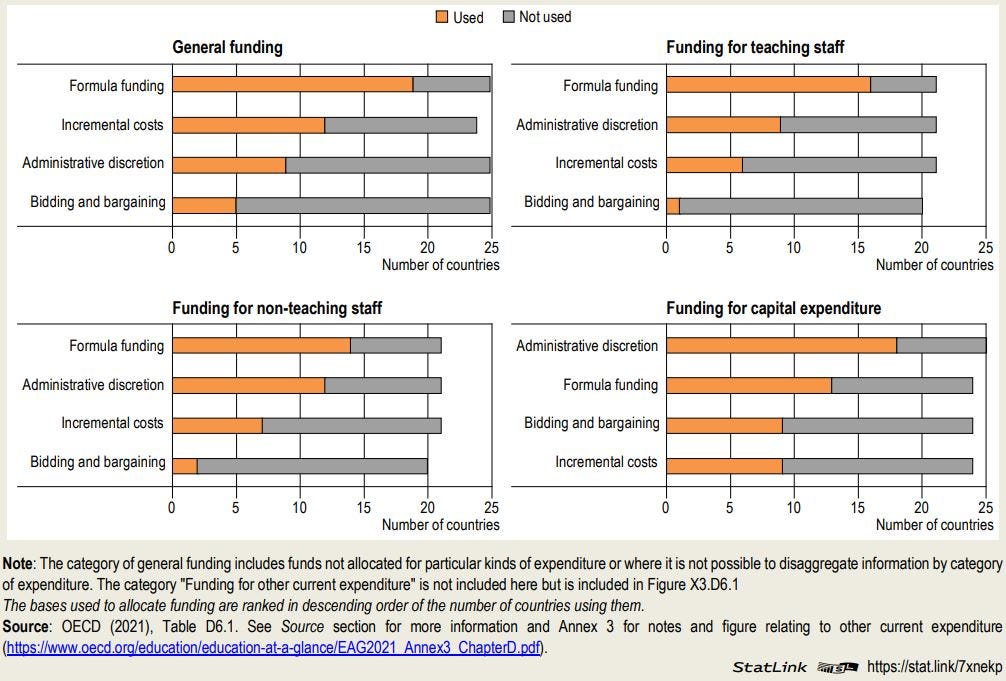
Use of funding formulas to allocate public funds
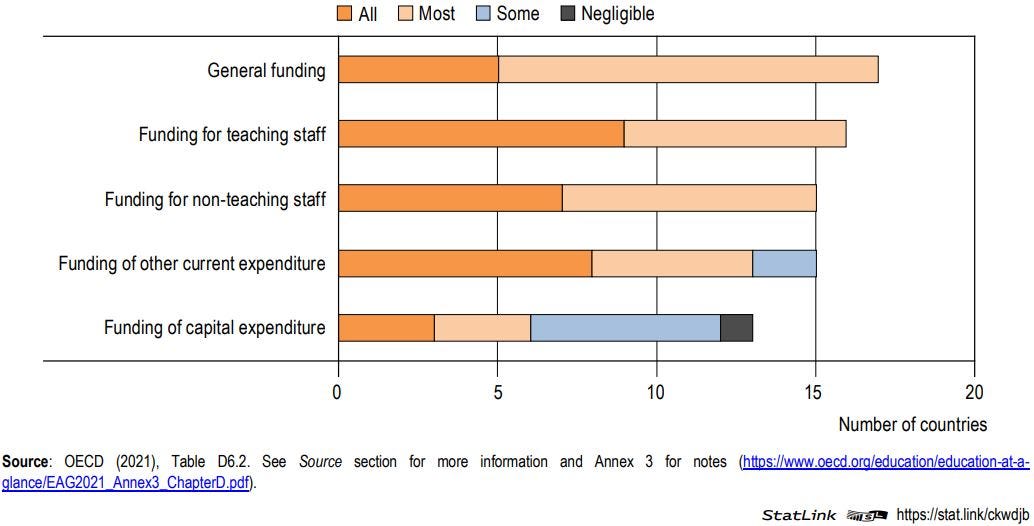
Funding formulas are the most commonly used basis for allocation of public funds to primary and lower secondary educational institutions among OECD countries and other participants. In the vast majority of countries, they are used by central or state governments to allocate all or most funding for all categories of expenditure, with the exception of funding for capital expenditure.
Proportion of public funding allocated by central or state governments to public primary educational institutions (or the lowest level of governance) using funding formulas, by category of funding (2019)
Related publications
-
 18 July 2024
18 July 2024 -
 12 July 2022
12 July 2022
Programmes and projects
-
Since 2013, the OECD has gathered evidence on how school resource policies work in different contexts. The focus is now on digital resources to enable countries to learn from each other in the digital transformation of their education.Learn more
-
The OECD Indicators of Education Systems (INES) programme seeks to gauge the performance of national education systems through internationally comparable data.Learn more
-
PISA is the OECD's Programme for International Student Assessment. PISA measures 15-year-olds’ ability to use their reading, mathematics and science knowledge and skills to meet real-life challenges.Learn more
-
The Education Policy Outlook is an analytical observatory that monitors the evolution of policy priorities and policy developments from early childhood education to adult education, mainly among OECD education systems, to provide a comparative understanding of how policies are evolving, and how they can be best implemented or improved over time.Learn more
-
The OECD’s programme on education and skills policy support policymakers in their efforts to achieve high-quality lifelong learning, which in turn contributes to personal development, sustainable economic growth, and social cohesion.Learn more
-
Education for Inclusive Societies Project is designed to respond to the increasing diversity that characterises education systems, and seeks to help governments and relevant stakeholders achieve more equitable and inclusive education systems as a pillar to create more inclusive societies.Learn more
-
Data and digital technologies are among the most powerful drivers of innovation in education, offering a broad range of opportunities for system and school management, as well as for teaching and learning. But they also create new policy issues as countries face challenges to reap the benefits of digitalisation in education while minimising its risks.Learn more
-
Preparing for the future means taking a careful look at how the world is changing. Reflecting on alternative futures helps anticipate and strategically plan for potential shocks and surprises.Learn more





