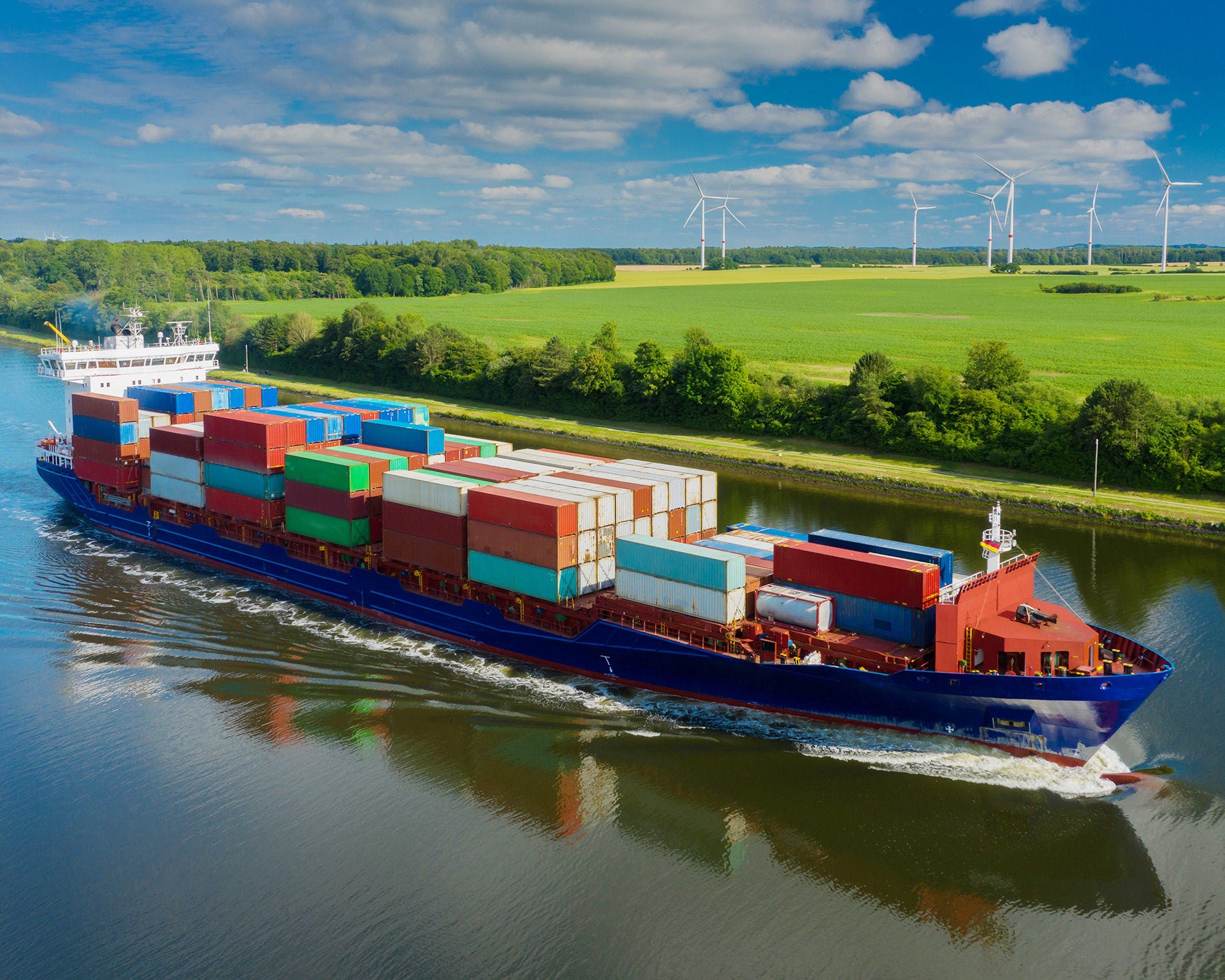
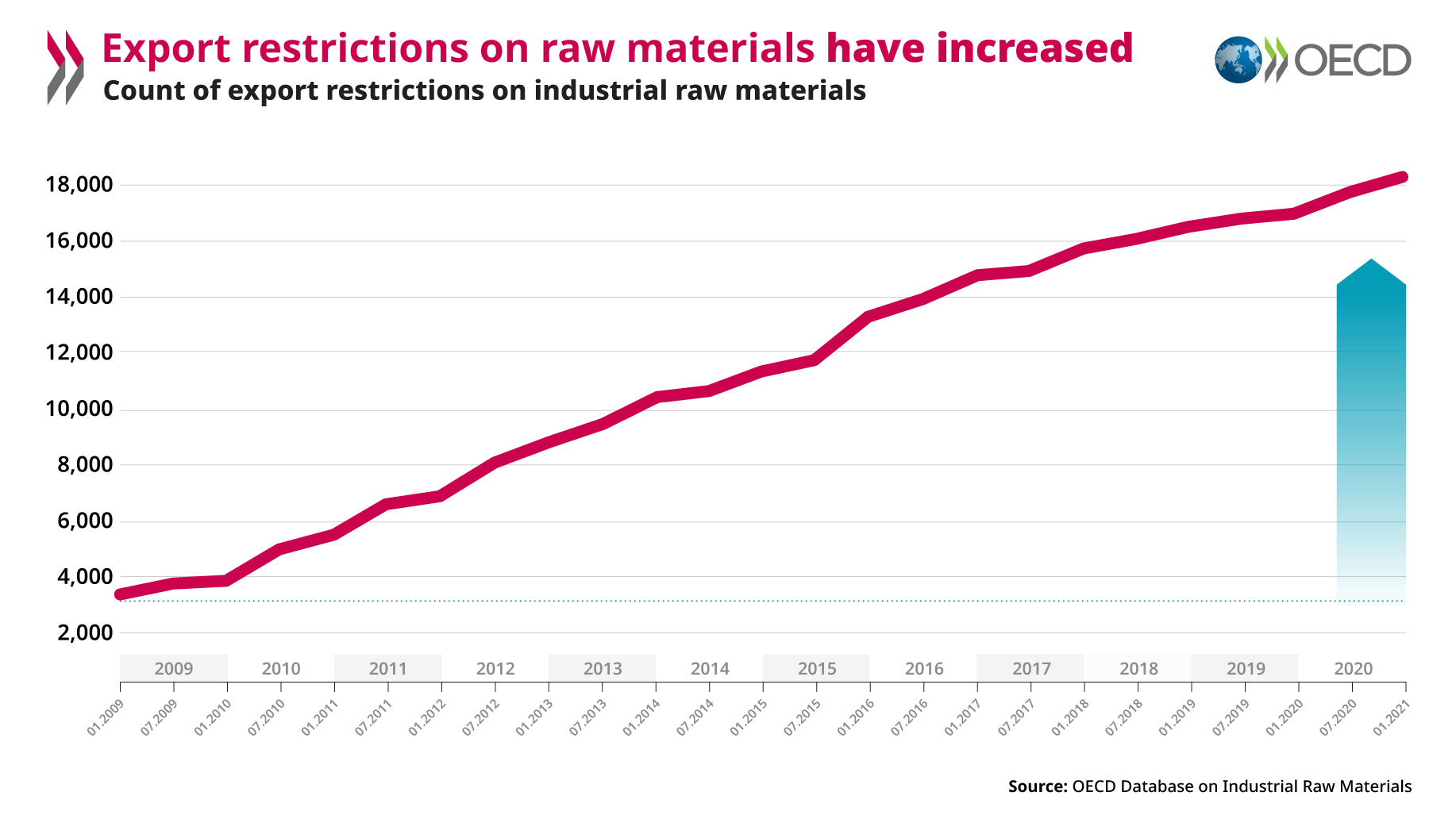
Government subsidies play a role in addressing market failures, such as underinvestment in technologies to mitigate climate change. Yet, if not well-designed, subsidies could not only fail to achieve environmental or other legitimate policy objectives, but may also undermine competitive markets, both domestically and internationally. The OECD hosts one of the most comprehensive sets of data on government support for agriculture, fisheries, manufacturing sectors and fossil fuels. A comprehensive research agenda combined with stakeholder consultations aims at analyzing both the environmental impacts of existing subsidies as well as the use of subsidies for environmental goals, with a view to enhance policy makers’ understanding about how to address the speed and scale of the green transition, meeting distributional objectives and minimizing the distortive effects on trade.
Trade and sustainability
OECD work on trade and sustainability contributes to enhancing the understanding of how trade and the environment interact and to documenting and examining the effect of trade policies and trade-related environmental policies on trade, climate change, biodiversity loss and pollution. In particular, we look at how trade facilitation can ensure environmental goods and services cross borders smoothly and that trade-related environmental policies do not hamper trade more than necessary.