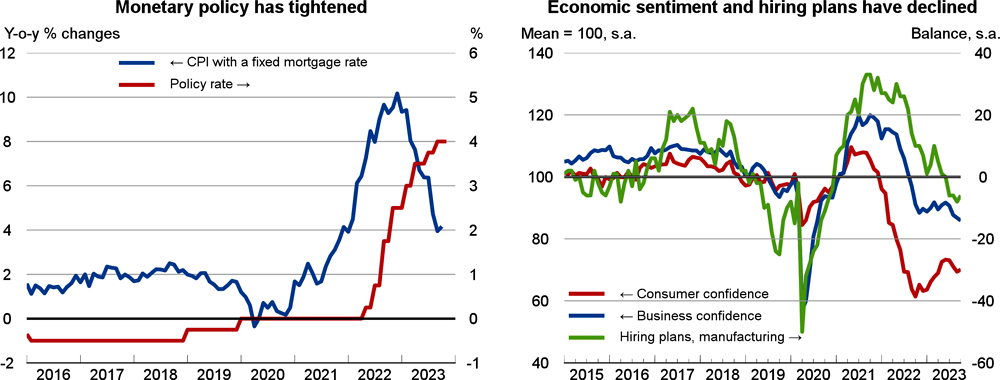
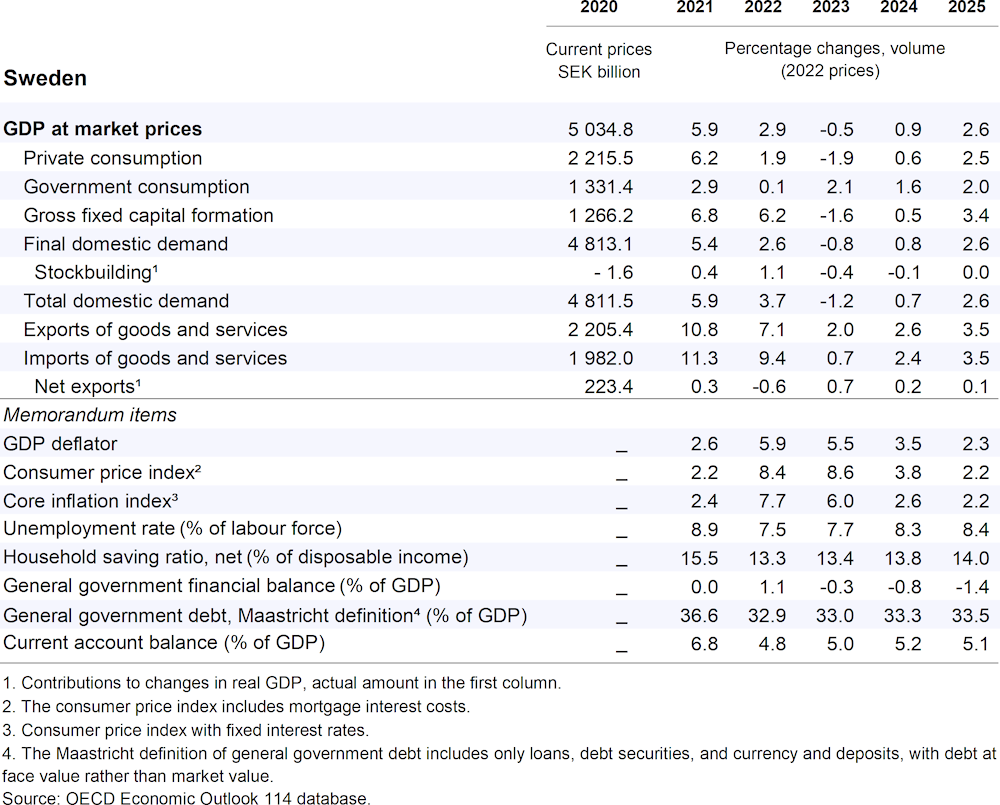
After a projected 0.5% contraction in 2023, GDP is projected to rise by 0.9% in 2024 and 2.6% in 2025. In the near term, elevated inflation will continue to weigh on households’ real disposable income and private investment, which is also held back by higher construction costs and declining demand for manufactured goods. Private consumption growth is expected to start regaining momentum in early 2024 as real disposable incomes start recovering.
Monetary policy should remain restrictive until inflation is clearly moving towards target. Continued fiscal restraint would help to combat inflation and maintain fiscal space. Tax reform, including aligning property taxes more closely with market values and phasing out mortgage interest deductions would improve tax efficiency and fairness. Loosening rent controls and other reforms facilitating mixed-background neighbourhoods, equal opportunities in schools, and the integration of disadvantaged groups into the labour market remain priorities.