The SME Policy Index is a benchmarking tool designed to assess policies that support small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) in emerging economies and monitor progress in policy implementation over time. The index was developed in 2006 by the OECD in partnership with the European Commission, the European Bank for Reconstruction and Development (EBRD) and the European Training Foundation (ETF). Since then, it has been applied 10 times, covering 33 economies in 4 regions: the Western Balkans and Turkey (WBT), Eastern partnership countries, North African and Middle East regions, and the Association of Southeast Asian Nations countries. For the WBT region, it is structured around the ten principles of the Small Business Act for Europe (SBA), providing a wide range of pro-enterprise measures to guide the design and implementation of SME policies in the European Union.
While a number of other indices and benchmarking reports have been used to assess the business environment in the WBT region, the SME Policy Index follows a holistic approach that provides policy makers with an analysis of their strengths and weaknesses in SME-related policy settings, allowing comparisons to be made across economies and measuring convergence toward OECD and EU good practice1. The report also monitors alignment in enterprise policy with the EU acquis, especially with respect to Chapter 20, and provides inputs into the Economic Reform Programmes (ERPs), most notably under the business environment structural dimension.
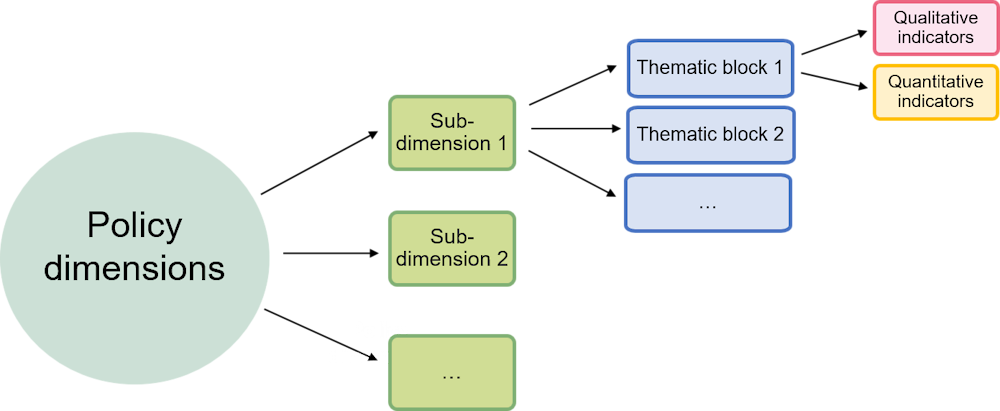
The SME Policy Index is divided into 12 regional policy chapters and 7 economy-specific profiles, which contain individualised structural reform recommendations tailored to the specific challenges of each WBT economy.