Education policies should prioritise being responsive and flexible across different areas, including study pathways, school choice, curriculum design and teaching strategies. Flexibility enables schools to tailor their curriculum, create spaces for innovation and address local challenges effectively. Study pathways need to be organised and implemented in a way that responds to the needs of both students and the labour market, with a flexible combination of vocational and academic choices while maintaining consistent quality. Additionally, the teaching practices employed in classrooms significantly impact student learning.
Education equity
Equitable education systems ensure that every student can achieve their educational potential regardless of their personal or social circumstances. Governments need to prioritise equity and inclusion in education and recognise their importance in paving the way for students to have equal chances for success in the future.

Key messages
Most countries explicitly aim to improve access, quality, equity and efficiency in their education systems. However, fulfilling these objectives is a challenge for policy makers. The pursuit of equity and efficiency has often been presented as a trade-off when it comes to the allocation of resources in education. Nevertheless, efficiency and equity can go hand in hand. Drawing from the insights and policies in OECD countries, focusing on four areas can help improve both equity and efficiency: investing in high-quality early childhood education and care, improving teacher quality, reducing educational failure rates, and adapting school networks to changing demand.
Teaching is increasingly carried out in classrooms where students with a diverse range of experiences and needs come together. To create equitable and inclusive environments that support all learners, teachers need to be equipped with a range of competences, knowledge and attitudes. Without adequate learning opportunities, teachers often feel unprepared to address the diverse needs of students. Furthermore, school leaders play an important role in facilitating equitable and inclusive teaching, and are central actors in shaping and driving the effective implementation of practices for equity and inclusion.
Context
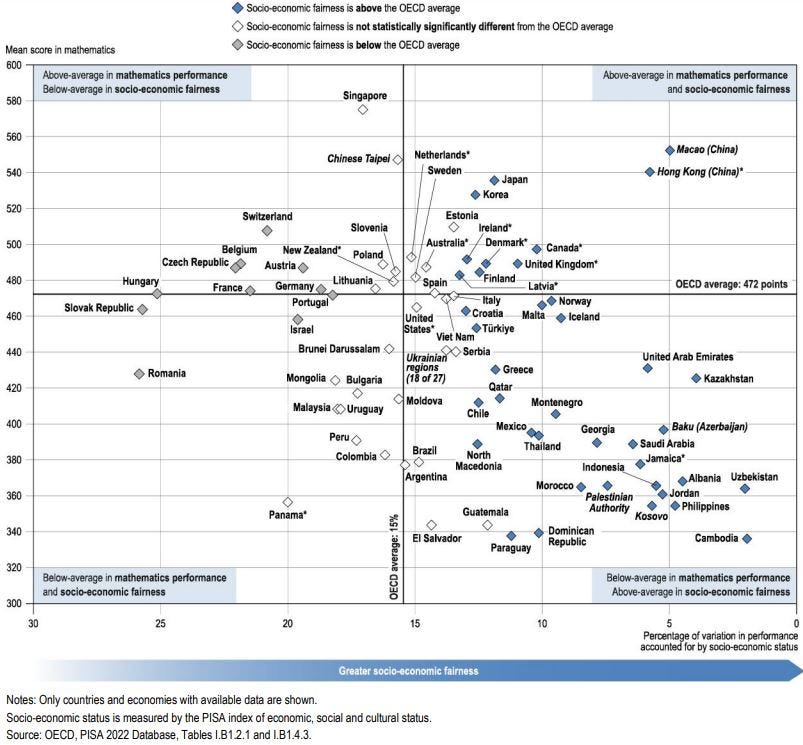
Students’ socio-economic status accounts for a significant share of the variation in performance
On average across OECD countries, 15% of the variation in mathematics within each country is associated with socio-economic status. An education system is fairer when this relationship is weaker. In eight countries and economies, socio-economic status accounts for 20% or more of the variation. By contrast, socio-economic status accounts for less than 7% of the variation in 14 countries.
Strength of socio-economic gradient and mathematics performance (2022)
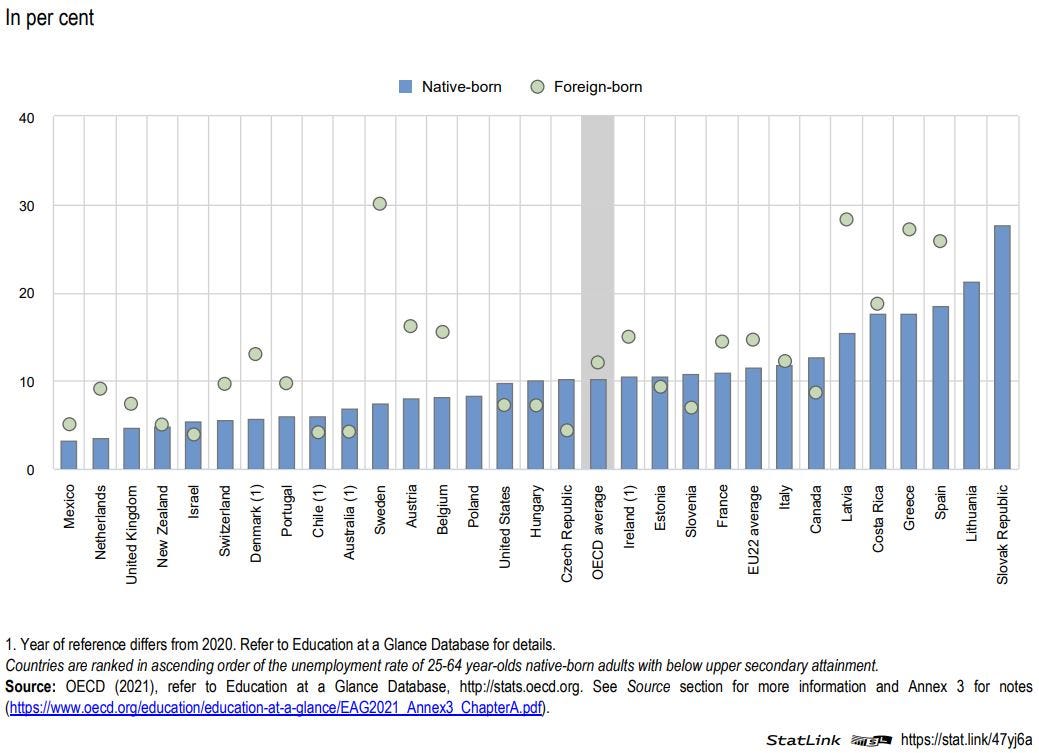
Labour market outcomes for foreign-born adults compared to native-born adults vary across OECD countries
The likelihood of being employed increases with educational attainment, but it increases more steeply for native-born than for foreign-born adults. This is also reflected in higher unemployment rates among foreign-born adults. On average across OECD countries, the unemployment rate was 12% for foreign-born adults without upper secondary attainment, and 10% among their native-born peers.
Unemployment rates of 25-64 year-olds with below upper secondary attainment, by migration status (2020)
Latest insights
-
 Press release10 September 2024
Press release10 September 2024
Related publications
-
 12 November 2024
12 November 2024
Programmes and projects
-
Education for Inclusive Societies Project is designed to respond to the increasing diversity that characterises education systems, and seeks to help governments and relevant stakeholders achieve more equitable and inclusive education systems as a pillar to create more inclusive societies.Learn more
-
PISA is the OECD's Programme for International Student Assessment. PISA measures 15-year-olds’ ability to use their reading, mathematics and science knowledge and skills to meet real-life challenges.Learn more
-
Understanding the nature of 21st Century childhood is crucial for an education that is increasingly expected to support students to thrive in both a digital and non-digital world, delivering academic learning while also building physical and emotional well-being. This has implications for the skills, capacity and resources required.Learn more
-
The OECD Career Readiness project is designed to provide new advice to governments, schools, employers and other stakeholders on how to best prepare young people to compete in an ever-changing labour market.Learn more
-
The Early Childhood Education and Care (ECEC) programme conducts analysis and develops new data to support countries in reviewing and improving their early childhood services and systems.Learn more
-
The OECD’s programme on education and skills policy support policymakers in their efforts to achieve high-quality lifelong learning, which in turn contributes to personal development, sustainable economic growth, and social cohesion.Learn more
-
OECD Future of Education and Skills 2030 aims to build a common understanding of the knowledge, skills, attitudes and values students need in the 21st century.Learn more
-
The OECD Indicators of Education Systems (INES) programme seeks to gauge the performance of national education systems through internationally comparable data.Learn more
-
The Survey of Adult Skills, a product of the PIAAC, measures adults’ proficiency in literacy, numeracy and the ability to solve problems in technology-rich environments.Learn more
-
The PISA-based Test for Schools provides school-level estimates of performance and information about the learning environment and students’ attitudes gathered from student questionnaires. Find out more and how schools and their networks can take part.Learn more
-
Since 2013, the OECD has gathered evidence on how school resource policies work in different contexts. The focus is now on digital resources to enable countries to learn from each other in the digital transformation of their education.Learn more
-
The Starting Strong Teaching and Learning International Survey (TALIS Starting Strong) is an international, large-scale survey of staff and leaders in early childhood education and care (ECEC).Learn more
-
TALIS - the Teaching and Learning International Survey - is the world's largest international survey about teachers and school leaders.Learn more
-
Preparing for the future means taking a careful look at how the world is changing. Reflecting on alternative futures helps anticipate and strategically plan for potential shocks and surprises.Learn more







