Disposable incomes of older people are on average lower than those of the total population. The over‑65s had incomes of 88% of that of the total population in 2020 on average, broken down into 93% for the 66‑75 age group and 81% for the over‑75s. Among the over‑65s, the range goes from about 70% or less in Estonia, Korea, Latvia and Lithuania to around 100% or more in Costa Rica, France, Israel, Italy, Luxembourg and Mexico. In two‑thirds of OECD countries, public transfers provide more than half of gross income after age 65.
Pensions at a Glance 2023

Incomes of older people
Key Results
People over 65 had incomes amounting to 88% of the overall average population incomes in 2020 or the latest year available on average across countries (Table 7.1). Older people fared best in Costa Rica, France, Israel, Italy, Luxembourg and Mexico in relative terms where incomes for the over‑65s were about or slightly higher than for the total population. Older people also had high relative incomes on average in Greece, Iceland, Portugal, Spain and Türkiye in international comparison. In Estonia, Korea and Lithuania, by contrast, the income of older people was about one‑third lower.
Average relative incomes tend to fall with age after retirement. Lower relative incomes for older retirees are partly explained by cohort effects given growth trends in real earnings across cohorts driven by productivity gains. Where pensions are indexed to average‑wage growth, pensions during retirement improve similarly; however, many countries index at a lower level than wage growth in normal times. While price indexation protects purchasing power, it tends to lower relative income over time, particularly affecting relatively those who live long including women. For the latter, this adds to their lower own entitlements due to lower past employment and wages compared to men. Moreover, older people live alone more often, which lowers their equivalised disposable income given household economies of scale.
The income of people aged over 65 has increased relative to that of the total population in more than two‑thirds of OECD countries over the last two decades, and on average by 6.7 percentage points across all countries for which data is available. Driven by a maturing pension system, the over‑65s in Israel have seen the strongest rise in their relative income, about 24 percentage points, from 81% in 2000 to 105% in 2020. Italy, Norway and Spain also record strong increases. The sharpest declines are reported in Poland (‑10 percentage points since 2005) and Chile (‑8 percentage points since 2006).
Sources of income
Of the four main sources of income on which older people draw, public transfers (earnings-related pensions, resource‑tested benefits, etc.) and private occupational transfers (pensions, severance payments, death grants, etc.) account for around two‑thirds of the total income (Figure 7.1). Public transfers account for 57% and private occupational transfers represent 7% of older people’s incomes on average. The countries where over‑65s are most reliant on public transfers are Austria, Belgium, Finland and Luxembourg: more than 80% of their incomes come from that source. Public transfers represent only 10% and 18% of all income in Mexico and Chile, respectively. Private occupational transfers are relevant in 13 OECD countries, with the Netherlands being highest at 40%.
Work accounts for 26% and capital for about 10% of older people’s incomes on average. Work is especially important in Chile, Korea and Mexico, where it accounts for around half of old-age income; it also represents a large share of income in Costa Rica, Estonia, Iceland, Japan, Latvia, Lithuania, New Zealand, Poland, the Slovak Republic and the United States. Also, as incomes are measured at the household level, work is likely to be a more important income source for older people where many of them live in multi-generational households.
Capital, mostly private pensions, represents over 40% of all income sources of older people in Canada. In Denmark, Korea and the United States, capital represents over 20% of all income.
Definition and measurement
Incomes of older people groups all incomes from employment, self-employment, capital and public transfers. The data shown are for disposable incomes (i.e. net of personal income tax and social security contributions). Incomes are measured on a household basis and equivalised with the square‑root equivalence scale to adjust for differences in household size. See OECD Income Distribution Database for more details on definitions and data sources. The special chapter on “Incomes and poverty of older people” in OECD (2013) provides a more detailed analysis.
Further reading
OECD (2023), Income Distribution Database, http://www.oecd.org/social/income-distribution-database.htm.
OECD (2019), Will future pensioners work for longer and retire on less?, OECD, Paris, https://www.oecd.org/pensions/public-pensions/OECD-Policy-Brief-Future-Pensioners-2019.pdf.
OECD (2013), Pensions at a Glance 2013: OECD and G20 Indicators, OECD Publishing, Paris, https://doi.org/10.1787/pension_glance-2013-en.
Table 7.1. Incomes of older people, 2020 or latest available year
Average income by age group in percentage of average income of total population
|
|
All aged over 65 |
Age 66‑75 |
Aged over 75 |
Change for all aged over 65 since 2000 or earliest thereafter |
|
All aged over 65 |
Age 66‑75 |
Aged over 75 |
Change for all aged over 65 since 2000 or earliest thereafter |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Australia |
76.9 |
81.6 |
69.8 |
7.6 |
Korea |
68.0 |
75.3 |
58.6 |
|
|
Austria |
94.5 |
97.3 |
90.9 |
7.4 |
Latvia |
72.0 |
80.6 |
60.4 |
‑0.5 |
|
Belgium |
77.7 |
81.7 |
72.6 |
Lithuania |
67.4 |
71.5 |
63.0 |
‑5.8 |
|
|
Canada |
89.3 |
91.8 |
85.2 |
0.8 |
Luxembourg |
110.1 |
112.4 |
106.4 |
|
|
Chile |
93.5 |
95.8 |
90.0 |
‑8.0 |
Mexico |
102.3 |
106.5 |
95.6 |
16.1 |
|
Colombia |
Netherlands |
79.2 |
85.3 |
69.8 |
‑5.4 |
||||
|
Costa Rica |
104.1 |
109.3 |
95.9 |
New Zealand |
80.1 |
86.5 |
69.7 |
8.9 |
|
|
Czechia |
77.3 |
80.3 |
72.2 |
‑1.1 |
Norway |
90.0 |
99.5 |
77.0 |
18.8 |
|
Denmark |
82.0 |
86.9 |
75.0 |
10.6 |
Poland |
85.7 |
85.5 |
86.0 |
‑10.0 |
|
Estonia |
69.0 |
75.3 |
61.3 |
Portugal |
95.7 |
102.6 |
88.1 |
15.3 |
|
|
Finland |
83.6 |
89.2 |
75.9 |
5.3 |
Slovak Republic |
86.6 |
88.5 |
82.9 |
6.8 |
|
France |
99.8 |
103.9 |
94.5 |
1.9 |
Slovenia |
86.5 |
86.9 |
85.9 |
2.2 |
|
Germany |
87.6 |
90.2 |
85.3 |
‑0.4 |
Spain |
99.0 |
107.7 |
89.2 |
18.0 |
|
Greece |
96.9 |
104.7 |
87.4 |
15.3 |
Sweden |
86.5 |
98.1 |
71.9 |
8.4 |
|
Hungary |
87.0 |
89.0 |
83.7 |
0.0 |
Switzerland |
80.8 |
86.4 |
74.2 |
‑0.9 |
|
Iceland |
95.0 |
103.8 |
77.5 |
14.6 |
Türkiye |
97.3 |
101.0 |
90.6 |
7.1 |
|
Ireland |
83.0 |
89.1 |
73.8 |
13.0 |
United Kingdom |
86.4 |
90.5 |
81.0 |
13.4 |
|
Israel |
105.2 |
110.7 |
96.2 |
23.7 |
United States |
93.2 |
99.1 |
83.8 |
10.1 |
|
Italy |
103.0 |
111.6 |
94.2 |
17.5 |
|||||
|
Japan |
85.2 |
91.8 |
78.0 |
‑4.5 |
OECD |
88.0 |
93.2 |
80.9 |
6.7 |
Notes: Most recent data are for 2020 except for the following countries: Costa Rica, Finland, Latvia, the Netherlands, Norway, Sweden and the United States (2021), Denmark, France, Germany, Hungary, the Slovak Republic, Switzerland and Türkiye (2019), Japan (2018) and Chile and Iceland (2017).: Data for 2000 except for Greece and Türkiye (2004), Chile and Switzerland (2006), Czechia, Iceland, Ireland, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Portugal, the Slovak Republic and Slovenia (2005), Austria and Spain (2007). Due to a break in series, 2006‑data for Chile are scaled with a factor measuring the age‑specific effect of the series break on income levels using data from 2011 or closest available. Historical data for Belgium, Estonia, Korea and Luxembourg are not comparable due to breaks in series and those for Costa Rica are unavailable and are not shown here. Data for Colombia is unavailable.
Source: OECD Income Distribution Database, www.oecd.org/social/income-distribution-database.htm (June 2023 version).
Figure 7.1. Income sources of older people, 2020 or latest available year
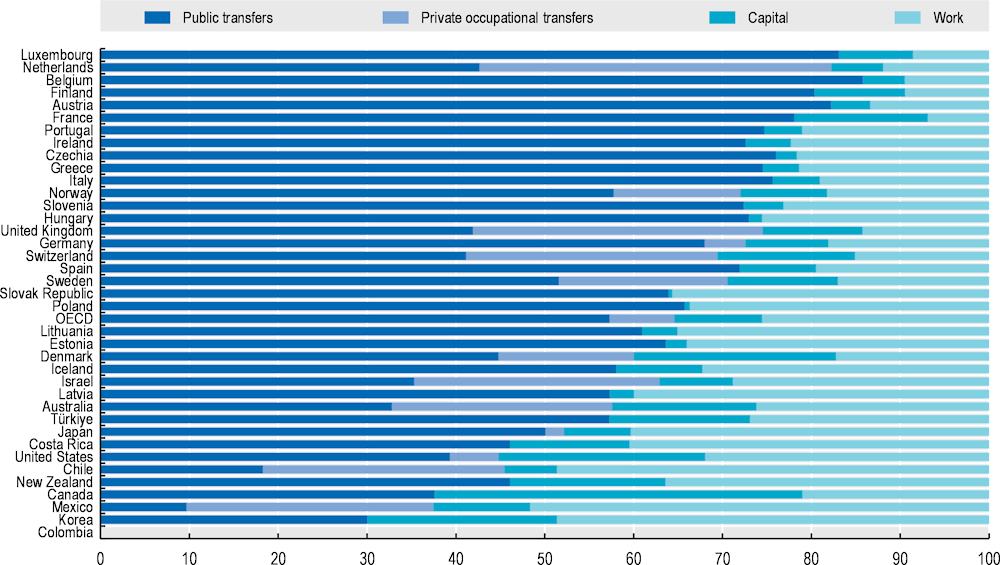
Note: Income from work includes both earnings (employment income) and income from self-employment. Private occupational transfers include pensions, severance payments, death grants and other. Capital income includes private personal pensions and income from the returns on non-pension savings. Data are for 2020 except for some countries; see note of Table 7.1.
Source: OECD Income Distribution Database, www.oecd.org/social/income-distribution-database.htm (June 2023 version).