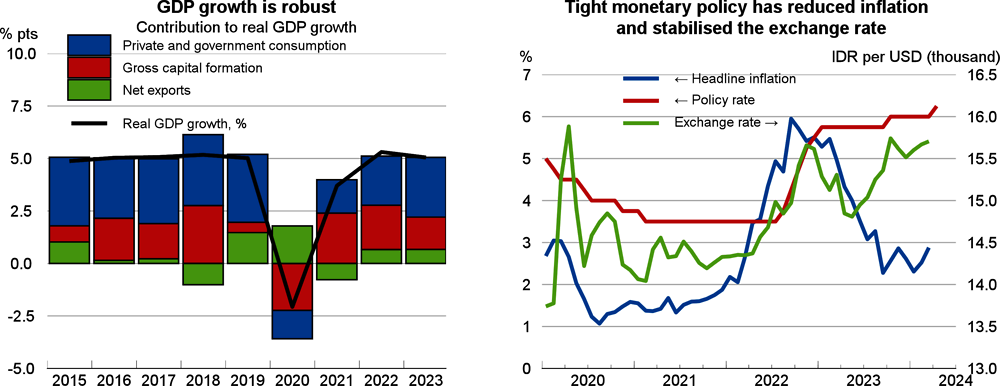
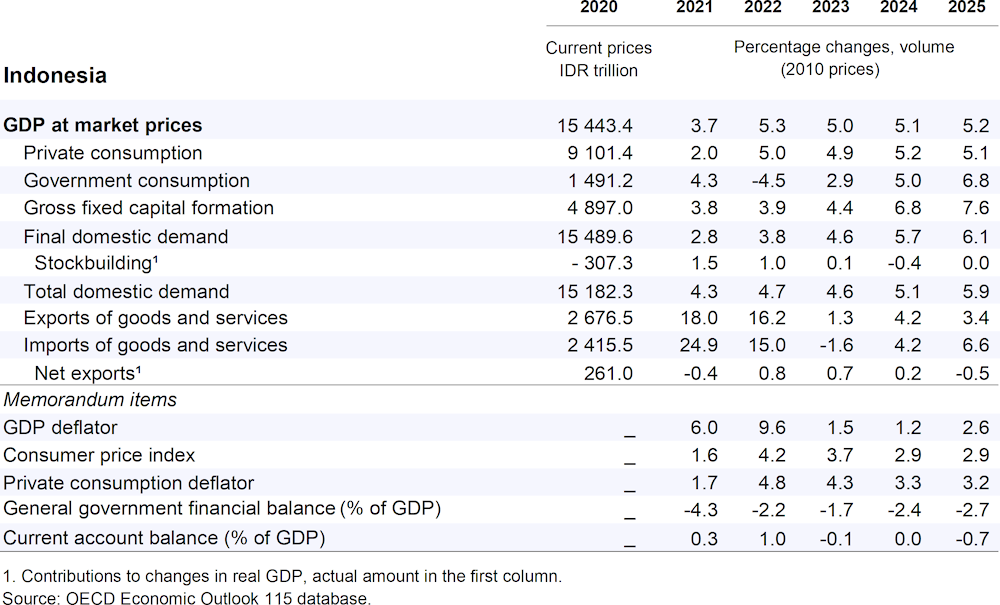
GDP growth is projected to be 5.1% in 2024 and 5.2% in 2025. Domestic demand remains driven by private consumption and gross capital formation growth will strengthen in 2024 and 2025. Headline inflation is expected to fall slightly below 3% in 2024 and remain unchanged in 2025, within the central bank’s revised target corridor (1.5-3.5%). Heightened global uncertainty and lower commodity prices have reduced nominal merchandise exports. Although the current account deficit is growing, international reserves are expected to be broadly stable.
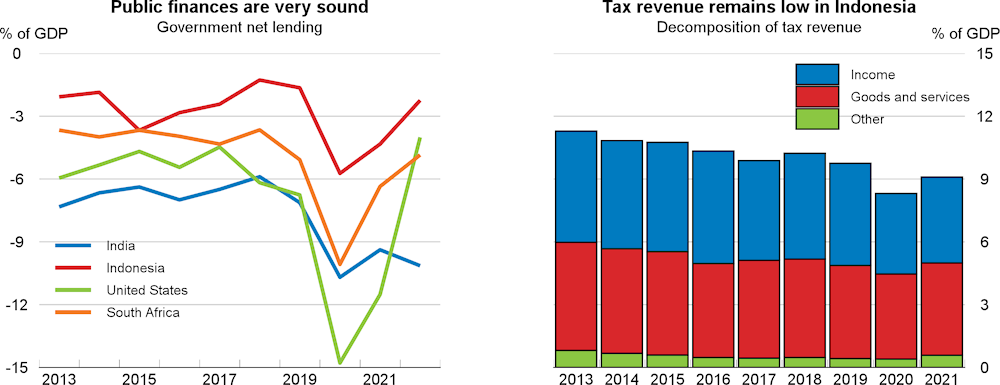
Following an unexpected policy rate rise in April, prompted by currency weakening, monetary policy easing is projected to start in late 2024, as disinflation continues. With a new administration taking office in October 2024 committed to additional social spending, fiscal policy is projected to be mildly expansionary, although complying with the 3% of GDP constitutional deficit limit. Longer‑term fiscal sustainability would be helped by further tax-base broadening and improved tax compliance and efforts to ensure efficient government spending, including through tightly focused support for vulnerable households. Supporting the transition to net-zero and enhancing energy security should remain priority goals.