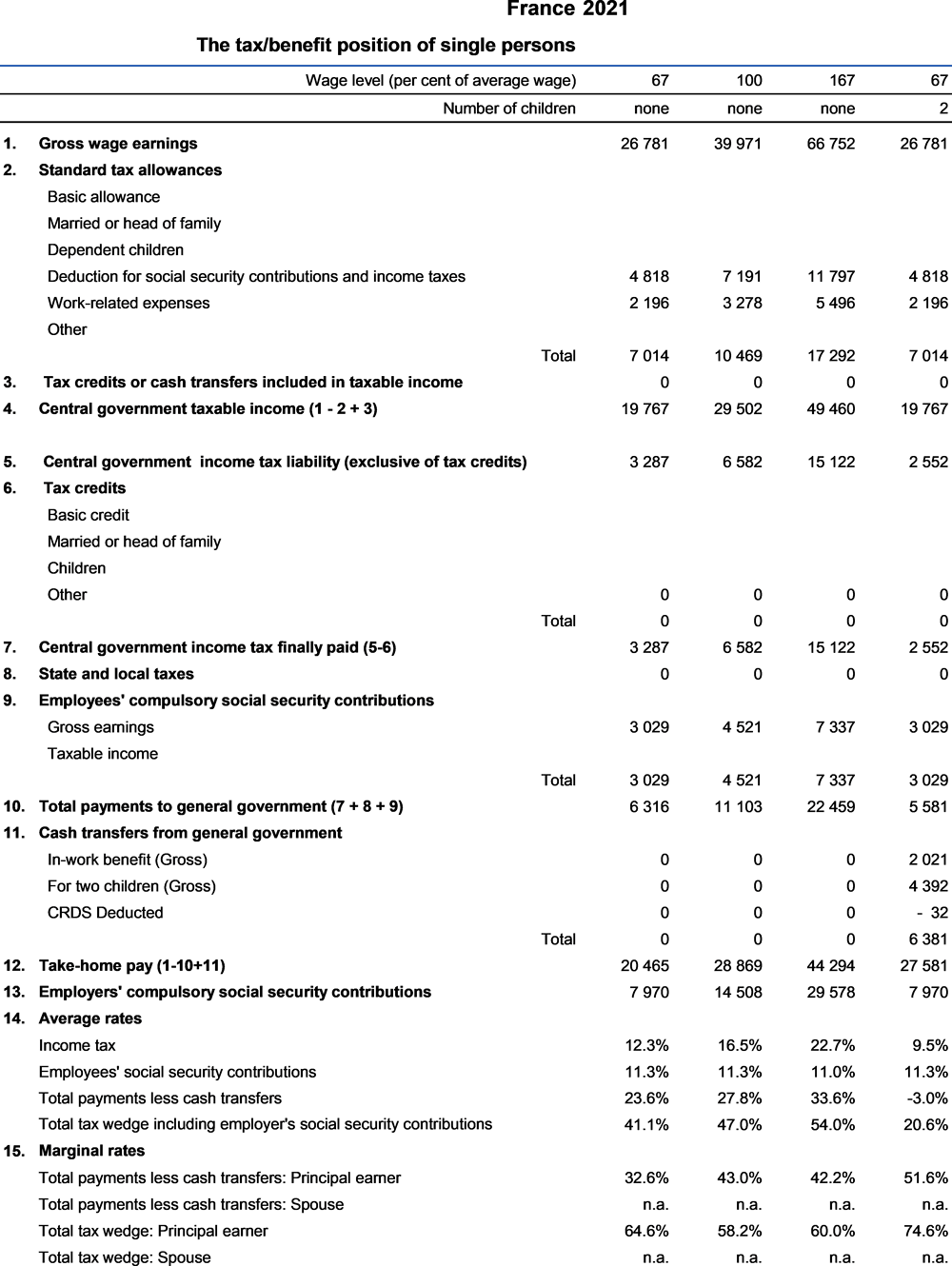
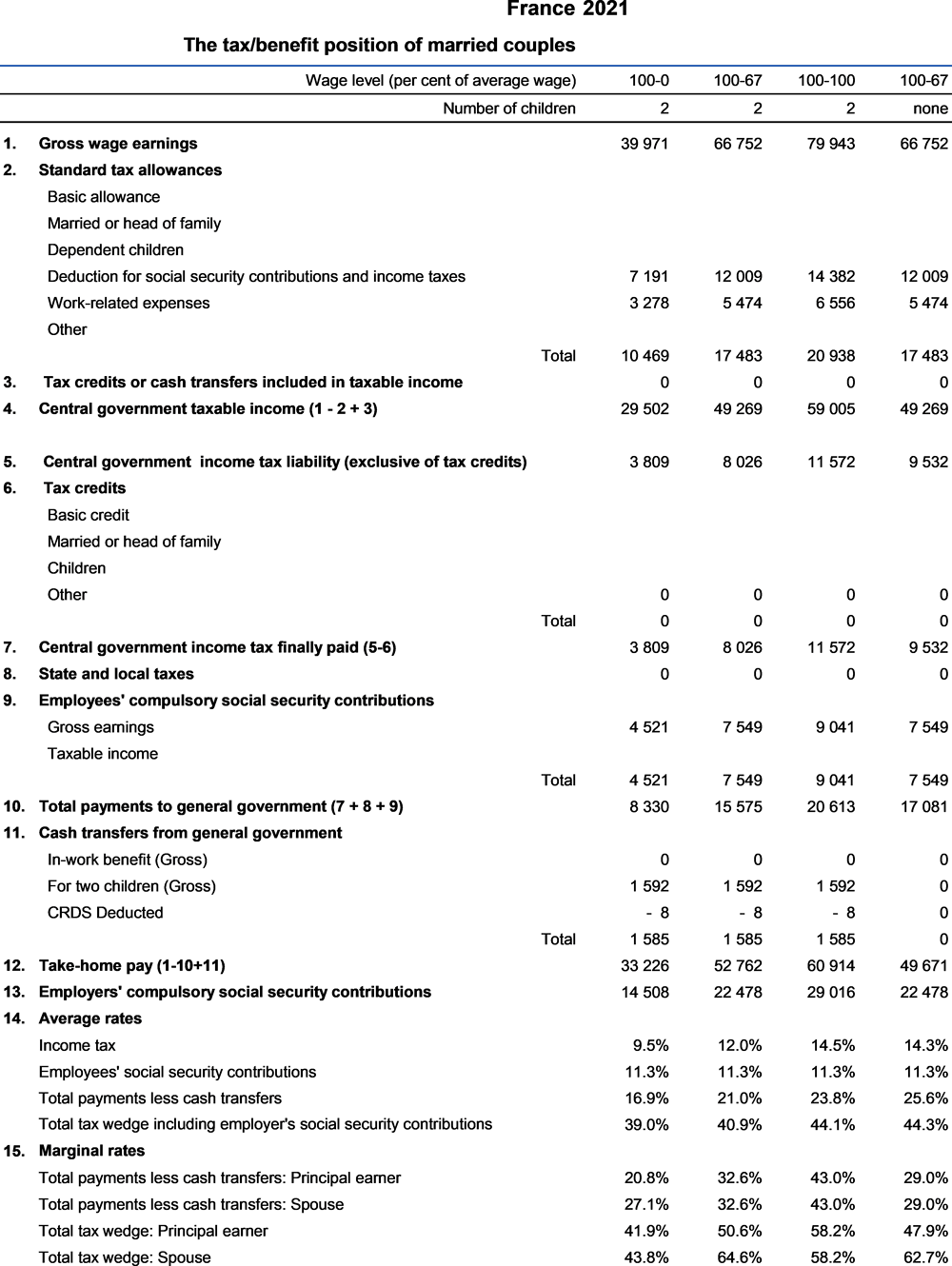
The reduction of employer-paid social insurance contributions, introduced in 1993, has been gradually extended and strengthened. As of 2021, it includes two types of measures:
(i) The general reduction of employer-paid social insurance (ex-“Fillon Act”, also called today “zero contributions URSSAF”) is a decreasing reduction in social security contributions, which eliminates all common law social contributions paid at the minimum wage and whose level decreases with wage to become zero for a gross annual wage equal to 1.6 times the gross annual minimum wage. It applies irrespective of the number of hours worked for workers with contracts of at least three months. Since 1st January 2021, the maximum reduction is at 32.46% for companies with more than 50 employees. For companies with less than 50 employees, it is 32.06% since 1st January 2021.
(ii) A proportional reduction in health insurance and family allowance contributions, which allow for a reduction of 6 and 1.8 percentage points respectively for gross annual wage below 2.5 and 3.5 times the gross annual minimum wage. The 6 percentage point’s reduction replaces since 1st January 2019 the competitive tax credit (CICE – crédit d’impôt pour la compétitivité et l’emploi), whereas the 1.8 percentage point reduction was introduced in 2015 by the Responsibility Act (Phase 1).
The gross annual minimum wage (for 1 820 hours) was changed twice in 2021: it was at EUR 18 655 from January 1st 2021, and increased at EUR 19 074 from October 1st 2021.