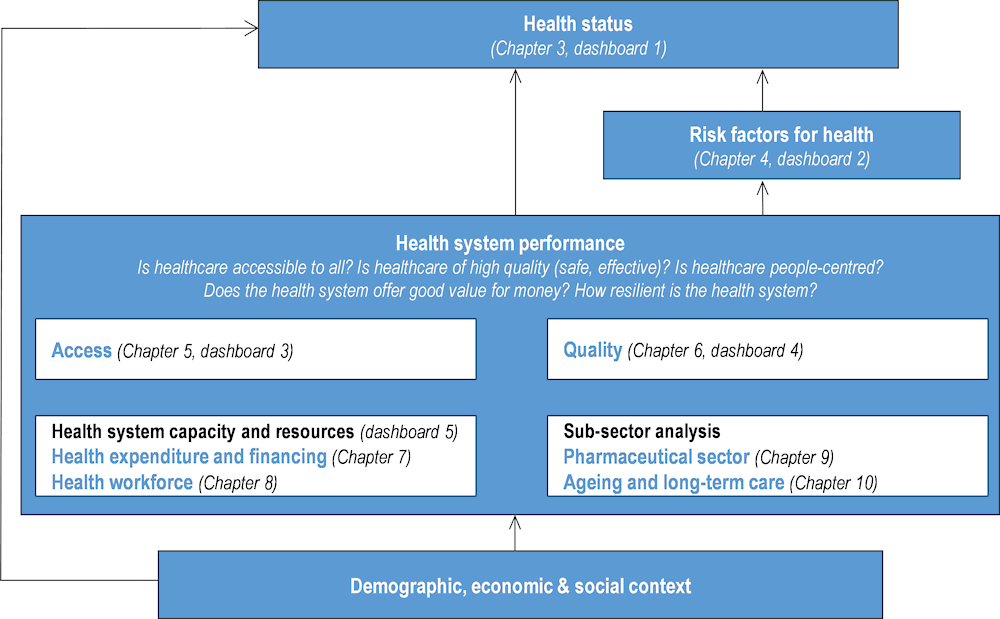
Health at a Glance 2023 compares OECD countries on each component of this general framework. It is structured around ten chapters. Chapter 1 presents an overview of health and health system performance, based on a subset of core indicators from the report. Chapter 2 offers a more in-depth analysis on a particular theme, which in this edition is on digital health.
The next eight chapters then provide detailed country comparisons across a range of health and health system indicators. Where possible, time trend analysis and data disaggregated by demographic and socio‑economic characteristics are included. Chapter 3 on health status highlights cross-country differences in life expectancy, the main causes of mortality, mental health, self-assessed health, and other indicators of population health. Chapter 4 analyses risk factors for health such as smoking, alcohol, obesity, and environmental health risks. Chapter 5 on access investigates the affordability, availability, and use of services, with special attention given to socio‑economic inequalities. Chapter 6 assesses quality and outcomes of care in terms of patient safety, clinical effectiveness, and whether healthcare is responsive to people’s needs. Indicators across the full lifecycle of care are included, from prevention to primary, chronic and acute care. Chapter 7 on health expenditure and financing compares how much countries spend on health, how such spending is financed, and what funds are spent on. Chapter 8 examines the health workforce, particularly the supply and remuneration of doctors and nurses. Chapter 9 takes a closer look at the pharmaceutical sector. Chapter 10 focuses on ageing and long-term care. This includes factors that influence the demand for long-term care, and the availability of high-quality health services.